Scaling SQL databases in the cloud is a critical practice for organizations aiming to optimize performance and accommodate increasing workloads. By leveraging cloud infrastructure, businesses can easily adjust resources such as CPU, storage, and memory to handle fluctuations in traffic and data volume. This approach enables improved scalability, high availability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises solutions. However, selecting the right scaling strategy and tools is essential to ensure database performance and reliability in the cloud environment.
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, scaling SQL databases in the cloud has emerged as a critical factor for businesses seeking to enhance performance, improve reliability, and decrease costs. With cloud computing becoming the norm, understanding how to effectively scale SQL databases is essential for ensuring your applications meet user demand.
Understanding SQL Database Scaling
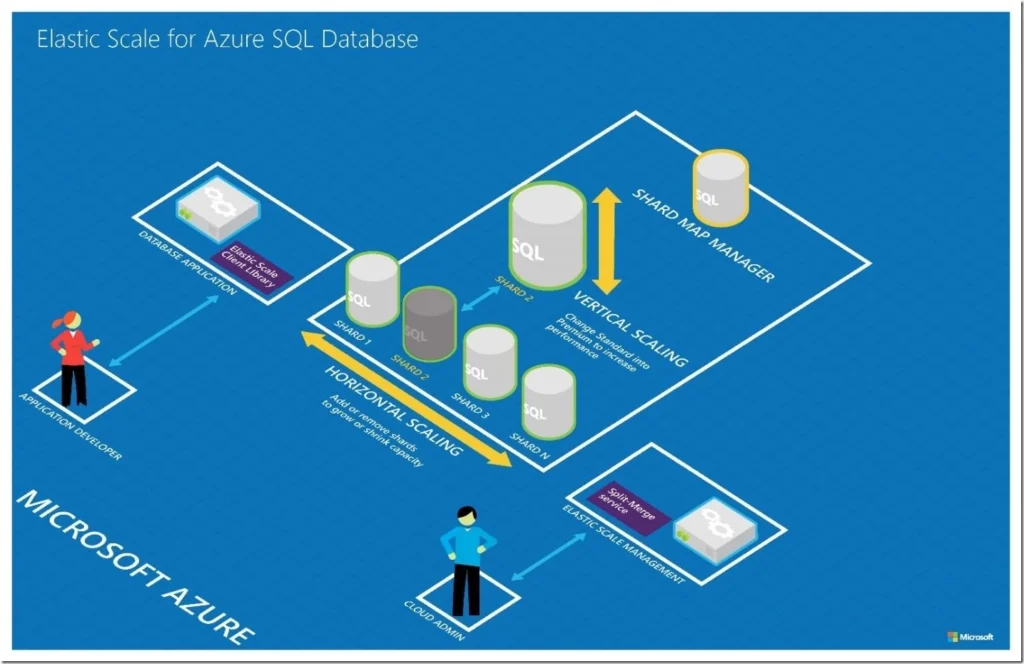
Before diving into the mechanics of scaling SQL databases in the cloud, it’s important to comprehend the basic concepts. Scaling can be categorized into two types: vertical scaling and horizontal scaling.
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, also known as scale-up, involves enhancing the resources of an existing server. This could include increasing the CPU, RAM, or storage. Vertical scaling is typically simpler as it requires less reconfiguration of the application. However, it has limitations because every server has a maximum capacity.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling, or scale-out, refers to adding more servers to your database infrastructure. This approach offers greater flexibility and can lead to a more resilient system. However, it introduces complexity in terms of database management, including synchronization and consistency across multiple nodes.
Why Cloud for SQL Databases?
Cloud platforms offer a variety of benefits for SQL database management, including:
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models reduce upfront costs.
- Scalability: On-demand scaling capabilities adjust resources to match workload.
- High Availability: Cloud providers ensure uptime through redundancy and failover strategies.
- Resource Management: Automated resource allocation optimizes performance.
Key Considerations for Scaling SQL Databases
When planning to scale SQL databases in the cloud, consider the following:
1. Database Type
Different SQL databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server, have unique scaling capabilities and limitations. Choose the database that aligns with your scaling requirements.
2. Workload Patterns
Analyze the workload patterns of your application. Understanding peak usage times can inform your scaling strategy, allowing you to allocate resources efficiently during high-demand periods.
3. Cloud Provider Features
Investigate the features provided by your cloud vendor. Options like Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, and Azure SQL Database come with integrated scaling tools, automated backups, and security features.
Strategies for Scaling SQL Databases
Multiple strategies can be employed to effectively scale SQL databases in the cloud:
1. Read Replicas
Utilizing read replicas allows you to offload read traffic from the primary database, which enhances performance. It works particularly well for applications with heavy read operations.
2. Database Sharding
Sharding is the process of distributing data across multiple database instances. Each instance, or shard, holds a portion of the overall data, leading to improved performance and management as each shard can be scaled independently.
3. Connection Pooling
Implementing connection pooling helps manage database connections more efficiently. This technique reduces the overhead of opening and closing connections, thus improving application performance and reducing server load.
4. Caching Mechanisms
Employing caching mechanisms, such as Redis or Memcached, can significantly reduce the load on your SQL database by storing frequently accessed data in memory for faster retrieval.
Monitoring and Performance Tuning
To ensure optimal performance when scaling SQL databases in the cloud, regular monitoring and performance tuning are essential:
1. Performance Metrics
Track performance metrics such as query response times, resource utilization, and transaction rates to identify potential bottlenecks in your database.
2. Automated Scaling
Consider using automated scaling solutions provided by cloud vendors. This feature allows your database to dynamically adjust resources based on current workloads, ensuring cost efficiency without sacrificing performance.
3. Index Optimization
Optimize database indices to improve query performance. Proper indexing can drastically reduce data retrieval times, directly impacting application speed.
Case Studies: Successful SQL Database Scaling
Several companies have effectively scaled their SQL databases in the cloud:
1. Netflix
Netflix employs various cloud services to handle millions of data points daily. By leveraging cloud-based SQL databases, Netflix can seamlessly manage its user data and viewing habits, ensuring a smooth user experience.
2. Airbnb
Airbnb utilizes PostgreSQL to scale its database effectively. By implementing techniques such as read replicas and sharding, they have managed to support their global infrastructure efficiently.
Best Practices for Scaling SQL Databases in the Cloud
To maximize your success when scaling SQL databases, adhere to the following best practices:
- Design for Scalability: From the outset, design your database schema and architecture with scalability in mind.
- Regularly Review Performance: Perform periodic reviews of your database’s performance metrics and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Stay Updated with Technology: Keep up with the latest advancements in cloud technology and SQL database features.
- Employ a Backup Strategy: Ensure you have a robust backup strategy in place to protect your data during scaling operations.
By implementing the right strategies and best practices, scaling SQL databases in the cloud can be a straightforward process that greatly enhances your application’s performance, availability, and reliability. As you think of moving your SQL database to the cloud or optimizing your existing one, ensure that you leverage the powerful tools and features your cloud provider offers to make the most out of your database management.
Scaling SQL databases in the cloud offers a flexible and efficient solution for accommodating growth and optimizing performance. By leveraging cloud technologies, organizations can easily adjust resources, improve scalability, and enhance reliability to meet evolving business needs. It is clear that cloud-based solutions provide valuable advantages for managing SQL databases in today’s dynamic and competitive environment.