In the realm of Big Data, data warehousing plays a pivotal role in the storage, integration, and management of vast amounts of data generated by various sources. Data warehouses are designed to provide a centralized repository for structured and unstructured data, enabling organizations to efficiently store, analyze, and extract valuable insights from their data assets. By leveraging data warehousing capabilities in the context of Big Data, businesses can enhance decision-making processes, improve operational efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven landscape. This article explores the significance of data warehousing in the era of Big Data and discusses its critical impact on driving innovation and business success.
In the age of Big Data, organizations are inundated with vast amounts of information generated from diverse sources. To harness the power of this data, businesses turn to data warehousing as a pivotal strategy. Understanding the role of data warehousing in big data is essential for organizations looking to gain insights, improve decision-making, and maintain a competitive edge.
What is Data Warehousing?
Data warehousing involves the central storage of large volumes of data collected from various sources. This process includes data cleaning, transformation, and integration to provide users with a unified view of their data. By creating a repository, businesses can efficiently query and analyze historical data to inform future strategies.
Characteristics of Data Warehousing
Data warehousing is characterized by the following key features:
- Subject-Oriented: Data warehouses are designed around key subjects (such as sales, finance, etc.) rather than focused on specific applications.
- Integrated: Data warehouses consolidate data from multiple sources to provide a coherent view.
- Time-Variant: They maintain historical data, allowing organizations to track changes over time.
- Non-Volatile: Once data is entered, it remains stable over time, facilitating analytical processes.
Big Data Challenges Addressed by Data Warehousing
Organizations face numerous challenges when dealing with big data. Data warehousing offers solutions to some of these critical issues:
1. Data Volume
The sheer size of data generated can be overwhelming. Data warehouses optimize storage and retrieval, ensuring that big volumes of data can be effectively managed without degrading performance.
2. Data Variety
Big data comes from various sources – structured, unstructured, semi-structured, and more. Data warehousing facilitates the integration of diverse data types, allowing organizations to analyze and report on a consistent data set.
3. Data Velocity
With data being generated at an unprecedented speed, traditional databases often struggle to keep up. Data warehousing systems utilize innovative techniques to effectively load and process data, ensuring real-time analytics capabilities.
The Architecture of Data Warehousing
Understanding the architecture of data warehousing is critical for appreciating its role in big data:
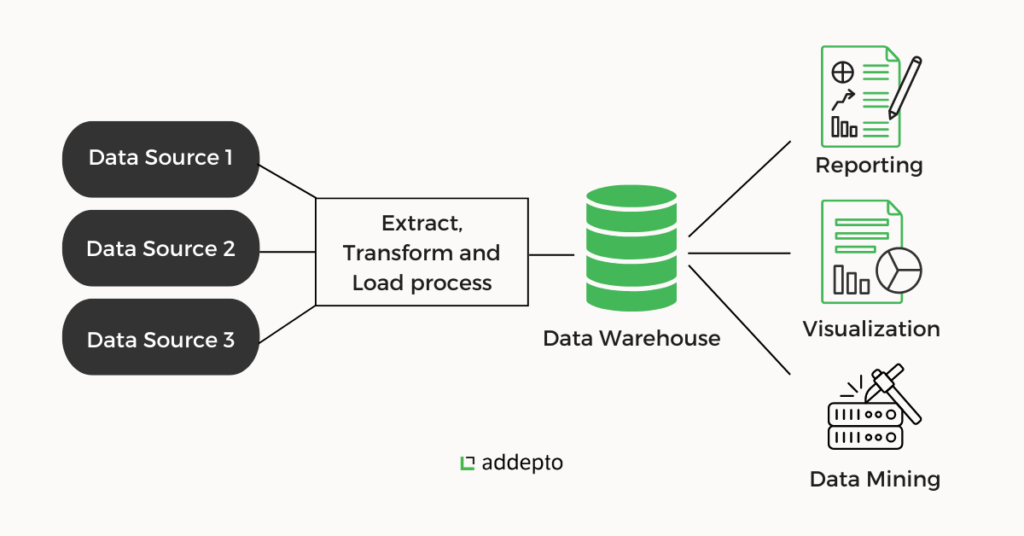
1. Data Source Layer
This layer includes various data sources such as transactional databases, CRM systems, social media, and external data. It is responsible for data collection and staging for processing.
2. ETL Process (Extract, Transform, Load)
The ETL process is vital in data warehousing. It involves:
- Extracting data from multiple sources.
- Transforming data into a usable format through cleansing and integration.
- Loading the organized data into the data warehouse for analysis.
3. Data Storage Layer
This is the core component where data is stored in a structured format, suitable for querying and analysis, often utilizing specific database technologies designed for big data environments.
4. Data Presentation Layer
The final layer provides access to end users and analysts, utilizing business intelligence tools for reporting and analysis. It helps in generating dashboards and visual insights that drive decision-making.
Benefits of Data Warehousing for Big Data Analytics
Organizations investing in data warehousing can experience a multitude of benefits:
1. Improved Decision-Making
Data warehousing provides decision-makers with accurate data analytics and reporting tools, allowing them to make informed decisions based on reliable data insights.
2. Enhanced Data Quality
By implementing strict data governance, data warehouses improve the accuracy and quality of data available for analysis, leading to better insights and strategic actions.
3. Historical Analysis
Data warehouses maintain historical records, enabling businesses to perform trend analysis over time, which is essential for forecasting and strategic planning.
4. Increased Business Intelligence
The ability to integrate data from various sources into a single repository enhances the scope of analytics, fueling robust business intelligence capabilities.
5. Cost Savings
While setting up a data warehouse can be significant, the long-term benefits, including improved efficiency and reduced data management costs, can lead to substantial savings for organizations.
Data Warehousing vs. Big Data Technologies
While both data warehousing and Big Data technologies like Hadoop or NoSQL databases serve data-centric purposes, they cater to different needs:
1. Structured vs. Unstructured Data
Data warehousing traditionally focuses on structured data, while big data technologies can manage and analyze unstructured data at scale, making them suitable for different types of analytics projects.
2. Batch Processing vs. Real-Time Processing
Data warehouses typically excel at batch processing of historical data, whereas big data technologies often allow for real-time data processing and analytics.
3. Use Cases
Data warehousing is most effective in areas where historical data analysis is crucial (like sales performance), while big data technologies are better for use cases involving massive datasets from various sources (like social media analytics).
Future Trends in Data Warehousing and Big Data
The landscape of data warehousing is continually evolving, especially in the context of big data. Here are some emerging trends:
1. Cloud-Based Data Warehousing
With the rise of cloud computing, organizations are increasingly migrating their data warehousing solutions to the cloud to benefit from scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
2. Data Virtualization
Data virtualization techniques allow for real-time access to data without requiring physical movement, creating opportunities for improved analytics across disparate sources.
3. AI and Machine Learning Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities into data warehousing solutions enables advanced predictive analytics, empowering data scientists and analysts to derive richer insights.
4. Real-Time Analytics
As organizations demand faster insights, the combination of data warehousing with stream processing technologies will pave the way for immediate decision-making capabilities.
Conclusion
In summary, data warehousing plays a crucial role in the big data landscape. As organizations continue to face challenges associated with data volume, variety, and velocity, the importance of data warehousing as a solution becomes increasingly clear. By understanding and leveraging the power of data warehouses, businesses can position themselves for success in a data-driven world.
Data warehousing plays a critical role in the realm of Big Data by providing a centralized repository for organizing, storing, and analyzing vast amounts of data. It acts as a foundational component that enables businesses to extract valuable insights and make informed decisions to drive growth and innovation in today’s data-driven world.