Over the past few decades, the field of Big Data has rapidly evolved, transforming the way businesses and organizations collect, store, and analyze vast amounts of data. This evolution has been marked by significant advancements in technology, tools, and methodologies that have enabled the processing and understanding of massive datasets at unprecedented scales. In this article, we will explore the past, present, and future of Big Data technologies, shedding light on how these innovations have shaped the way we harness data for insights and decision-making. From the early days of data warehouses to the modern era of cloud computing and machine learning, the journey of Big Data technologies has been nothing short of revolutionary. Join us as we delve into the exciting world of Big Data and uncover the transformative power it holds for the future.
The Past: The Birth of Big Data Technologies
In the early days of computing, data management was rudimentary at best. The term “Big Data” was not yet coined, and organizations primarily stored data in traditional relational databases. The emergence of the internet in the 1990s marked a significant turning point in data generation. Suddenly, vast amounts of unstructured data began to flow from various sources, including social media, e-commerce, and web logs.
The concept of Big Data began to take shape as technological advancements allowed for the storage and processing of larger datasets. Early data warehousing solutions, such as Oracle and IBM Db2, laid the groundwork for modern data management systems. However, these solutions struggled to handle the exponential growth of data.
In 2005, the term Big Data came into popular usage, driven by the need to analyze and make sense of vast data volumes. This marked the beginning of specialized Big Data technologies, with projects like Apache Hadoop emerging to address the challenges of scaling and processing large datasets.
The Present: The Rise of Advanced Big Data Technologies
Today, Big Data technologies have evolved dramatically and are now an integral part of the data ecosystem. A variety of tools and frameworks exist to help organizations store, process, and analyze data effectively.
1. Apache Hadoop and Ecosystem
Apache Hadoop remains a cornerstone of Big Data technology. It allows for distributed storage and processing of large volumes of data across clusters of computers. Hadoop’s architecture includes several key components:
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): A scalable storage system that provides high-throughput access to application data.
- MapReduce: A programming model for processing large datasets in parallel.
- YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): A resource management layer that schedules and manages resources across applications.
2. NoSQL Databases
As organizations began to manage unstructured data more effectively, NoSQL databases gained traction. Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL systems, including MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis, provide greater flexibility and scalability. Key features of NoSQL databases include:
- Schema-less Design: Allows for dynamic data storage without a predefined structure.
- Horizontal Scalability: Enables easy addition of new nodes to accommodate growing data demands.
- High Availability: Provides fault tolerance and robust data distribution mechanisms.
3. Data Lakes
Another significant trend is the rise of data lakes. Unlike data warehouses, which store structured data, data lakes can accommodate structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, making them ideal for storage and exploration of diverse data types. Solutions like Amazon S3 and Azure Data Lake Storage have emerged to address this need.
4. Real-Time Data Processing
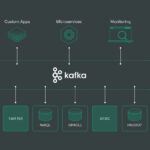
The demand for real-time analytics has driven the development of streaming data technologies. Tools such as Apache Kafka and Apache Flink are designed to manage real-time data streams, allowing organizations to draw insights on-the-fly and respond quickly to emerging trends and issues.
The Future: Trends Shaping Big Data Technologies
As we look ahead, several trends are poised to redefine the landscape of Big Data technologies in the coming years:
1. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are becoming ubiquitous in the realm of Big Data. These technologies are applied to large datasets to uncover patterns and derive insights without human intervention. Tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch are increasingly integrated into Big Data analytics pipelines, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions faster than ever.
2. Cloud-Based Big Data Solutions
Cloud computing continues to transform the storage and processing of Big Data. Platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure offer a host of Big Data services that allow organizations to scale resources as needed. This accessibility to powerful infrastructure empowers smaller enterprises to compete effectively.
3. Edge Computing
The proliferation of IoT devices generates immense amounts of data requiring real-time processing. Edge computing addresses this challenge by bringing computation and data storage closer to the data source. By processing data at the edge rather than relying solely on centralized cloud services, organizations can reduce latency and bandwidth consumption, leading to more efficient data processing.
4. Enhanced Data Privacy and Security
As data privacy regulations tighten globally, the emphasis on securing Big Data will intensify. Technologies such as advanced encryption, blockchain for data integrity, and identity and access management systems will play pivotal roles in ensuring that sensitive information remains protected and compliant with legal standards.
5. Explainable AI (XAI)
With the increasing integration of AI in data analytics, the demand for explainable AI is growing. Organizations and regulators are insisting on transparency in AI decision-making processes. As a result, the development of tools that clarify how models arrive at conclusions will be essential for building trust with users and stakeholders.
Conclusion: The Impact of Big Data Evolution
The evolution of Big Data technologies from rudimentary data management systems to complex analytics frameworks has fundamentally transformed how organizations operate. The ongoing advancements in AI, cloud solutions, edge computing, and data security are driving the future of Big Data, enabling businesses to harness the power of data in unprecedented ways. Embracing these innovations will not only facilitate improved decision-making but also open new avenues for growth in the digital age.
The evolution of Big Data technologies has been a remarkable journey, shaping the way data is collected, stored, and analyzed. From the early challenges of scalability and performance to the current focus on real-time analytics and machine learning, Big Data technologies have constantly evolved to meet the demands of an increasingly data-driven world. Looking ahead, the future of Big Data promises even greater advancements in areas such as edge computing, data privacy, and AI-driven insights, ensuring that Big Data technologies will continue to play a pivotal role in driving innovation and shaping the future of technology.