In the realm of Big Data, the efficient management and operation of data processing systems are paramount. Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration platform, has emerged as a powerful tool in enabling the seamless deployment, scaling, and maintenance of containerized applications. Central to this ecosystem are Kubernetes Operators, specialized controllers that extend the capabilities of Kubernetes to automate and manage complex applications. In the context of Big Data, Kubernetes Operators play a critical role in streamlining the deployment and management of data processing frameworks, such as Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and more, resulting in improved scalability, reliability, and efficiency in processing vast amounts of data. This article dives into exploring the significance of Kubernetes Operators in the Big Data landscape and their impact on optimizing data operations.
Kubernetes has revolutionized the way organizations manage applications through container orchestration. Particularly in the realm of Big Data, Kubernetes Operators serve a crucial role in simplifying, automating, and enhancing the management of complex applications and services.
What Are Kubernetes Operators?
A Kubernetes Operator is a method of packaging, deploying, and managing a Kubernetes application. Operators extend the Kubernetes API to manage resources and automate processes that would typically require human intervention. They encapsulate operational knowledge and allow developers to define how applications should be deployed and maintained, thereby enhancing the operational efficiency necessary for managing Big Data workloads.
Why Are Kubernetes Operators Essential for Big Data?
Big Data technologies often involve complex distributions and service dependencies. Here are some reasons Kubernetes Operators are essential in the Big Data ecosystem:
- Simplified Management: Operators automate routine tasks such as deployment, scaling, upgrades, and configuration management. This is vital in Big Data environments where application complexity can grow rapidly.
- Consistency and Reliability: Kubernetes Operators ensure that applications are deployed in a consistent manner, reducing the risk of human error and improving system reliability.
- Scalability: Big Data workloads often require significant scale adjustments. Operators can automatically scale applications up or down in response to real-time data processing needs.
- Declarative Configuration: Operators leverage Kubernetes’ declarative configuration model, allowing teams to specify the desired state of their applications. This ensures that the actual state of the application is always aligned with the desired state.
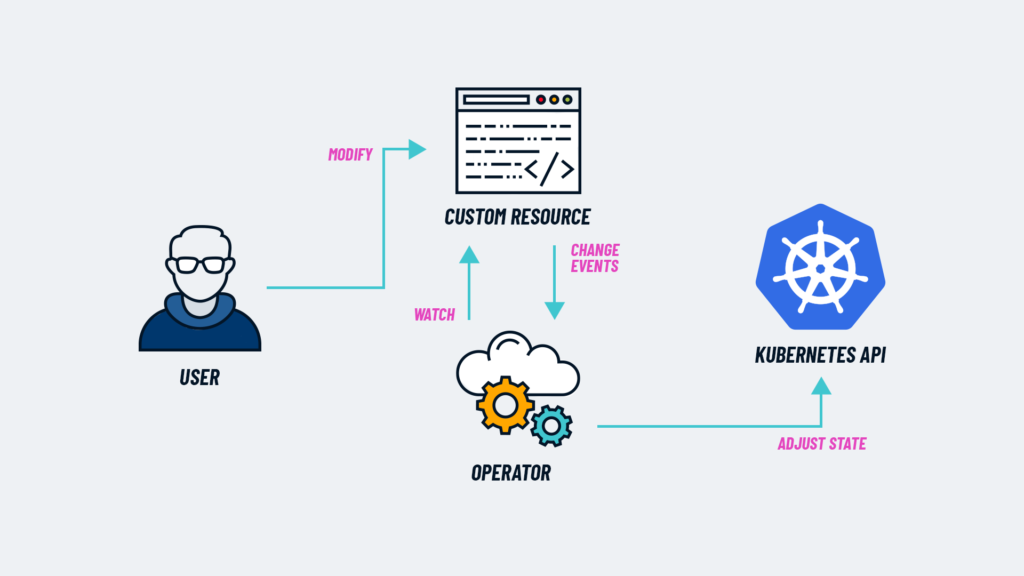
How Kubernetes Operators Work
Kubernetes Operators are built using two core components:
- Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs): Operators manage custom resources which extend Kubernetes’ API. This flexibility allows you to define new kinds of objects that represent your specific Big Data components, such as data pipelines or databases.
- Controller: The controller is a control loop that watches your custom resources and makes changes as needed, ensuring that the current state matches the desired state defined in the CRDs. It acts on events that occur in the Kubernetes environment, such as changes in resource usage or failed components.
Popular Big Data Use Cases for Kubernetes Operators
Kubernetes Operators have become pivotal in various Big Data scenarios. Here are some popular use cases:
1. Managing Distributed Databases
Operators can simplify the lifecycle management of distributed databases such as Apache Cassandra or MongoDB. They automate tasks like data replication, backup, restore, and failure recovery, thus reducing administration overhead.
2. Orchestrating Data Pipelines
For organizations leveraging tools like Apache Spark or Flink, Operators streamline the deployment and monitoring of data processing jobs, enabling real-time data analytics and batch processing without the need for manual intervention.
3. Stream Processing
Operators can assist in managing stream processing services like Kafka. They can handle topics creation, scaling of brokers, and ensure resilience and recovery during downtime, facilitating continuous data flow.
Building a Kubernetes Operator for Your Big Data Workload
Developing an Operator for your specific Big Data application involves several steps:
1. Define Your Custom Resources
Begin by identifying the key components of your Big Data application and define your own CRDs to encapsulate their configurations and operational needs.
2. Create the Operator Logic
Utilize programming frameworks such as the Operator SDK or Kubebuilder to create the logic that will manage your custom resources. This involves writing controllers that can respond to changes in the state of your resources.
3. Deploy and Test Your Operator
Once the Operator has been developed, deploy it to your Kubernetes cluster and perform extensive testing to ensure it behaves as expected under various conditions.
Benefits of Kubernetes Operators in Big Data Environments
Utilizing Kubernetes Operators within your Big Data environments offers numerous advantages:
- Operational Efficiency: Automates tedious management tasks, enabling data engineers to focus on strategic initiatives instead of routine maintenance.
- Faster Time-to-Market: By simplifying deployment and operational processes, teams can deliver data products and features more quickly.
- Integration with Cloud-native Ecosystem: Operators can easily integrate with other cloud-native tools and services, enhancing overall data architecture.
- Improved Resource Utilization: Dynamic scaling capabilities lead to optimized resource consumption and cost savings.
Challenges of Using Kubernetes Operators
While Kubernetes Operators provide significant benefits, organizations must also consider potential challenges:
- Complexity: Building a robust Operator necessitates a good understanding of Kubernetes internals and requires operational expertise in the Big Data stack being managed.
- Monitoring and Management: While Operators automate many tasks, they also introduce new components that require ongoing monitoring and management.
- Dependency Management: Managing dependencies between various Big Data components can be challenging, especially as deployments scale up.
Best Practices for Implementing Kubernetes Operators in Big Data
To ensure successful implementation of Kubernetes Operators in your Big Data ecosystem, adhere to the following best practices:
- Thorough Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation for your Operators to assist other developers and operations teams in understanding their functionalities.
- Incorporate Observability: Use monitoring tools to gain insights into Operator performance and to promptly identify issues.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously gather feedback and make iterative improvements to your Operator to adapt to changing requirements and best practices.
- Engage with the Community: Leverage community resources, forums, and support for knowledge sharing, and improvements, and to stay updated with the latest trends.
The Future of Kubernetes Operators in Big Data
The evolution of Kubernetes Operators is poised to significantly impact the Big Data landscape. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud-native architectures, the need for robust, efficient, and automated management tools will only grow.
As technologies mature and Kubernetes becomes a foundational element of IT infrastructure, the integration and role of Operators will likely expand, ushering in enhanced capabilities for Big Data workflows, including improved data governance, compliance, and security.
Kubernetes Operators play a crucial role in managing and automating complex Big Data applications in a scalable and efficient manner. By streamlining the deployment, management, and maintenance of Big Data workloads, Operators enable organizations to extract valuable insights and optimize performance from their data infrastructure. Embracing Kubernetes Operators is essential for harnessing the full potential of Big Data technologies in today’s data-driven world.