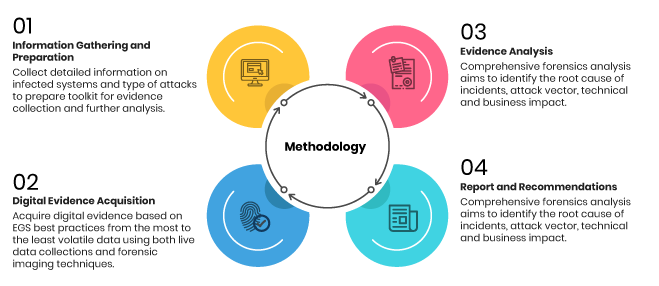
As the volume and complexity of data continue to increase exponentially in the era of Big Data, ensuring the security and integrity of this information has become a paramount concern for organizations across all industries. One crucial aspect of safeguarding Big Data is through the application of digital forensics, a specialized field that deals with the identification, preservation, analysis, and presentation of digital evidence. In the realm of Big Data security, digital forensics plays a critical role in investigating security incidents, identifying vulnerabilities, and responding to data breaches in a proactive and effective manner. By leveraging advanced forensic tools and techniques, organizations can uncover valuable insights, detect suspicious activities, and mitigate risks to protect their valuable data assets. This convergence of digital forensics and Big Data security paves the way for a more robust and comprehensive approach to safeguarding data in the digital age.
In today’s data-driven world, the significance of digital forensics in securing big data cannot be overstated. Big data encompasses vast amounts of information generated from various sources, and with its rapid expansion, the potential for security breaches also increases. Digital forensics serves as a pivotal defense mechanism in safeguarding the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of big data.
Understanding Big Data Security
Big data security involves a collection of processes, technologies, and strategies designed to protect large volumes of data from unauthorized access, breaches, and other threats. With numerous factors at play, ensuring the security of big data encompasses:
- Data Protection: Ensuring that sensitive information is appropriately secured and not exposed to potential data breaches.
- Data Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and trustworthiness of data throughout its lifecycle.
- Compliance: Adhering to various laws and regulations regarding data protection.
The Integration of Digital Forensics
Digital forensics involves the investigation, recovery, and analysis of data from digital devices to uncover evidence of criminal activities or breaches. Its integration into big data security strategies significantly enhances:
Incident Response and Investigation
When a data breach occurs, it is imperative to have an effective incident response plan in place. Digital forensics aids organizations in:
- Rapid Detection: Identifying the nature of a breach quickly, allowing for swift corrective actions.
- Evidence Collection: Gathering and preserving evidence systematically for potential legal proceedings.
- Root Cause Analysis: Determining how breaches occurred to prevent future incidents.
Data Recovery
In the event of a cyber-attack, critical data may be lost or compromised. Digital forensics provides recovery techniques that can restore data integrity, enabling organizations to:
- Recover Compromised Data: Restoring files or databases that have been damaged.
- Ensure Data Redundancy: Developing systems that duplicate data ensures that critical information is never permanently lost.
Forensic Analysis in Big Data Environments
Big data environments present unique challenges for forensic analysis. The sheer volume, velocity, and variety of data can complicate investigation efforts. However, advanced forensic techniques tailored to big data systems can:
Automate Data Processing
Automation technologies can enhance the efficiency of forensic analyses. By employing algorithms and machine learning techniques, organizations can:
- Filter Excess Data: Quickly eliminate irrelevant data from investigations.
- Identify Patterns: Analyze massive datasets to detect anomalies indicative of security incidents.
Utilizing Cloud Forensics
As organizations increasingly adopt cloud computing, understanding the role of cloud forensics becomes vital. Cloud forensics extends digital forensics to:
- Investigate Virtual Environments: Gather and analyze data stored in cloud infrastructures.
- Address Shared Responsibilities: Understand the division of security responsibilities between the cloud service provider and the user.
The Importance of Legal and Compliance Factors
Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, is critical for organizations handling big data. Digital forensics plays a substantial role in:
Maintaining Regulatory Compliance
Digital forensic investigations provide essential guidelines for organizations to follow legal protocols. It ensures that:
- Data Handling Procedures: Organizations have documented policies on data management and security.
- Incident Documentation: Investigations create records that demonstrate compliance with relevant laws.
Building a Response Framework for Legal Proceedings
In cases where data breaches result in legal actions, the documentation produced through digital forensics can be invaluable. It aids in:
- Expert Testimonies: Forensic experts can testify about the methods used in investigations.
- Data Integrity Verification: Establishing trustworthiness in data evidence presented in court.
Enhancing Security Protocols with Digital Forensics
The results of forensic investigations can lead to improved security policies within organizations. By analyzing the findings from incidents, organizations can:
Develop Proactive Security Measures
Understanding vulnerabilities through forensic analysis allows organizations to implement proactive security measures such as:
- Employee Training Programs: Educating teams about data security best practices.
- Incident Simulation Exercises: Regular drills to prepare for potential breaches.
Implementing Continuous Monitoring Systems
Digital forensics emphasizes the necessity for continuous monitoring of databases and networks to identify unusual activities proactively. Such systems can:
- Enable Real-time Alerts: Notify security teams of potential breaches as they occur.
- Facilitate Regular Audits: Ensure compliance with security policies and identify areas for improvement.
The Future of Digital Forensics in Big Data Security
As technologies evolve, the landscape of big data security will continue to change. Several advancements are likely to enhance the role of digital forensics:
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Utilizing artificial intelligence in digital forensics will enable faster data analysis and the identification of patterns that human analysts may miss. The adoption of AI can lead to:
- Predictive Analytics: Anticipating potential security threats before they manifest.
- Enhanced Data Filtering: More efficient sorting mechanisms for massive datasets.
Blockchain Technology for Data Integrity
Emerging technologies like blockchain may revolutionize how data integrity is verified. By creating immutable records, organizations can:
- Provide Traceable Audit Trails: Ensure that all data transactions are recorded and verifiable.
- Enhance Trustworthiness in Data Storage: Protect sensitive information from unauthorized changes.
The role of digital forensics in big data security is crucial in protecting sensitive information from threats and breaches. Its ability to investigate, recover, and analyze data makes it an integral part of the cybersecurity landscape. Organizations that adopt robust digital forensic strategies will be better equipped to navigate the complexities of big data, ensuring compliance, integrity, and trust in their data management practices.
Digital forensics plays a critical role in enhancing Big Data security by providing the tools and techniques necessary to investigate, analyze, and respond to security incidents. As the volume, variety, and velocity of data continue to grow, integrating digital forensics into Big Data security strategies is essential for detecting and mitigating threats effectively. By leveraging advanced forensic technologies and methodologies, organizations can better protect their valuable data assets and maintain trust with their stakeholders in the ever-evolving landscape of Big Data.