In the era of Big Data, where vast amounts of information are generated and collected every day, ensuring data integrity and compliance has become a critical concern for organizations. Data provenance, the ability to trace the origin and history of data, plays a crucial role in auditing and compliance efforts within the realm of Big Data. By tracking the lineage of data throughout its lifecycle, organizations can establish trust, accountability, and transparency in their data processes. This article explores the significance of data provenance in Big Data auditing and compliance, shedding light on its importance in maintaining data quality, ensuring regulatory adherence, and enhancing overall data governance practices.
In the emerging landscape of Big Data, data provenance has become a cornerstone for maintaining integrity and compliance. Understanding where data comes from, how it has been transformed, and who has accessed it are critical components in today’s data-driven ecosystem. The effective application of data provenance not only enhances data quality but also plays a pivotal role in auditing and ensuring regulatory compliance.
What is Data Provenance?
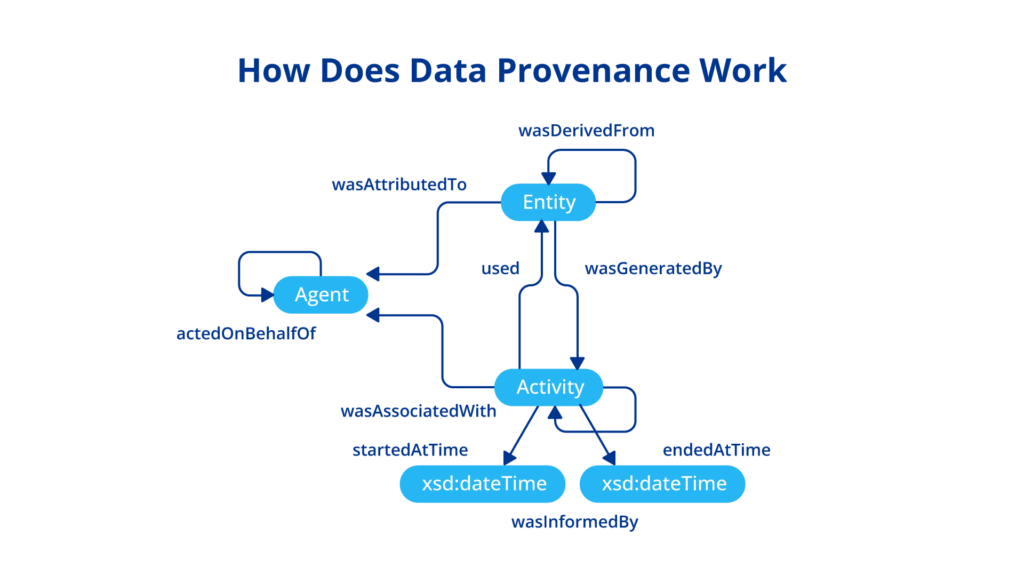
Data provenance refers to the documentation of the origins, changes, and movement of data throughout its lifecycle. It encompasses all the processes that data undergoes, including data collection, integration, transformation, and usage. Provenance can be visualized as a comprehensive map that tracks the lineage of data, which is crucial for understanding the context and significance of the information in question.
The Importance of Data Provenance in Big Data
With the exponential growth of data, organizations are faced with numerous challenges related to data management, especially pertaining to governance, quality, and security. Data provenance addresses these challenges by providing clarity and traceability.
Enhancing Data Quality
Data provenance contributes to improved data quality by allowing organizations to trace inconsistencies back to their source. When questionable data is flagged, provenance helps to verify the processes and transformations that occurred, enabling data stewards to rectify errors efficiently.
Facilitating Compliance with Regulations
Organizations in various sectors face stringent regulations around data use, such as GDPR in Europe and HIPAA in the U.S. By implementing data provenance practices, organizations can document their data handling processes effectively, ensuring compliance with legal requirements. Provenance records are vital in demonstrating how data is managed, processed, and stored, providing a clear audit trail for regulatory bodies.
Supporting Data Auditing and Accountability
Data auditing entails scrutinizing data management processes to ensure adherence to organizational policies and regulatory standards. Data provenance provides the necessary evidence needed during audits, allowing auditors to examine the lineage of data and confirm its accuracy and legality. Provenance details can show:
- Who accessed or modified the data
- When changes were made
- What transformations were applied
- Where the data originated
Implementation of Data Provenance in Big Data Systems
Integrating data provenance into big data systems is essential for effective data governance. Organizations can implement provenance in several ways, employing different technologies and methodologies.
Provenance Tracking Techniques
Various techniques can be utilized to track data provenance, including:
- Metadata capturing: Collecting metadata at each stage of data processing is crucial. This metadata includes information such as creation dates, modification timestamps, and user actions.
- Data lineage tools: Many tools are designed specifically for tracking data lineage. These tools can automate provenance tracking, making it easier to visualize data flows.
- Immutable logs: Recording data operations in immutable logs ensures a tamper-proof record of how data has been accessed and manipulated over time.
Leveraging Advanced Technologies
To effectively harness data provenance, organizations can leverage modern technologies:
- Blockchain technology: By using blockchain, organizations can create immutable and transparent records of data changes. This technology offers a decentralized way to verify data provenance without the risk of tampering.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and ML can analyze provenance data to detect anomalies and predict issues related to data quality and compliance proactively.
Challenges in Implementing Data Provenance
While the benefits of data provenance are clear, organizations may face several challenges during implementation:
Data Complexity
The sheer volume and complexity of big data make it difficult to maintain comprehensive provenance. As data is generated from multiple sources and undergoes numerous transformations, tracing its lineage can become cumbersome.
Resource Constraints
Implementing effective data provenance practices requires considerable resources, including skilled personnel and technological tools. Organizations may struggle with budget constraints when attempting to establish a robust provenance framework.
Data Privacy Concerns
Capturing extensive data provenance might conflict with privacy regulations, especially in cases where sensitive information is involved. Organizations must ensure that their provenance efforts do not inadvertently expose personal data.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Data Provenance in Big Data Auditing
Several organizations have successfully implemented data provenance to enhance their auditing processes and achieve compliance:
Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare industry, organizations need stringent compliance with healthcare regulations like HIPAA. One notable example is a healthcare provider that integrated data provenance into its electronic health records (EHR) system. This effort allowed for real-time tracking of patient data access and modifications, significantly improving audit trails and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Financial Institutions
In the finance sector, a major bank implemented a data provenance system to manage customer transaction data. The bank was able to create detailed logs showing the entire journey of data through its systems. This transparency not only improved regulatory compliance but also helped prevent fraud by allowing quick identification of anomalous transactions.
Future Trends in Data Provenance and Compliance
As the landscape of Big Data continues to evolve, several trends are emerging in data provenance:
Integration with Data Governance Frameworks
More organizations are integrating data provenance into their overall data governance frameworks. This trend promises to create a more cohesive approach to data management, enhancing both accountability and transparency.
Increased Automation and AI Adoption
With advancements in AI, automated data lineage tools are becoming more prevalent. These tools can automatically map data journeys, providing organizations with efficient ways to collect provenance information without manual efforts.
Emphasis on Ethical Data Practices
As concerns about data ethics grow, the role of provenance is likely to expand. Organizations will increasingly focus on ethical data sourcing and handling, with provenance serving as a key measure of responsible data use.
Ultimately, the role of data provenance in Big Data auditing and compliance cannot be overstated. By maintaining comprehensive records of data journey, organizations can fortify their auditing capabilities and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements while boosting data quality and security.
Data provenance plays a critical role in ensuring transparency, traceability, and trustworthiness of data in Big Data auditing and compliance. By tracking the origins and transformations of data throughout its lifecycle, organizations can establish accountability, detect anomalies, and comply with regulatory requirements. As Big Data continues to proliferate, leveraging data provenance mechanisms will be essential for maintaining data integrity and security in the digital age.