Apache Cassandra is a distributed NoSQL database known for its scalability and high availability, making it an ideal choice for real-time data analytics in the Big Data landscape. By efficiently handling large volumes of data across multiple nodes, Cassandra enables users to store, manage, and analyze vast amounts of data with low latency. In this guide, we will explore how to leverage Apache Cassandra for real-time data analytics, showcasing its features and best practices to harness the power of Big Data for insightful decision-making.
Understanding Apache Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is a highly scalable, distributed NoSQL database designed to handle large amounts of data across many commodity servers. This database excels in ensuring high availability with no single point of failure, making it an ideal choice for real-time data analytics within big data frameworks.
One of the core advantages of Cassandra is its ability to quickly ingest write-heavy loads while still offering high read performance. This makes it particularly suited for applications requiring real-time analytics where data can be ingested rapidly and queried with low latency.
The Data Model of Apache Cassandra
The data model of Cassandra is designed for performance at scale. It utilizes a log-structured merge-tree on disk and a flexible schema where data is organized in tables that can be queried efficiently. Some important concepts include:
- Column Families: These are similar to tables in relational databases.
- Rows: Each row in a column family can be uniquely identified by a primary key.
- Columns: Columns can vary from row to row, allowing for a wide variety of data types.
Setting Up Apache Cassandra
Installing Apache Cassandra can be straightforward if you follow the steps outlined below:
- Download Cassandra: Get the latest stable release from the official Apache Cassandra website.
- Install Java: Ensure you have the latest version of Java installed, as Cassandra is built on Java. Verify installation with the command
java -version. - Set Up Environment Variables: Define the `CASSANDRA_HOME` in your environment variables pointing to the Cassandra installation directory.
- Configure YAML File: Modify the
cassandra.yamlfile to define settings such as cluster name, seeds, listen address, etc. - Start Cassandra: Launch Cassandra using the command
bin/cassandra.
Data Ingestion for Real-Time Analytics
For effective real-time data analytics, you’ll need to focus on efficient data ingestion practices:
- Batch Processing: Utilize tools such as Apache Spark to batch process real-time data before sending it to Cassandra.
- Load Data Quickly: Use CQL (Cassandra Query Language) for rapid data insertion. Example:
INSERT INTO user_events (user_id, event_type, event_time) VALUES (123, 'click', '2023-01-01 12:00:00');Querying Data with CQL
Once your data is ingested into Apache Cassandra, you can perform quick queries using CQL, which resembles SQL:
- Selecting Data: Retrieve data based on specified conditions. For instance:
SELECT * FROM user_events WHERE user_id = 123 AND event_time >= '2023-01-01 00:00:00';This query takes advantage of Cassandra’s performance by utilizing primary keys and clustering columns to efficiently retrieve records.
Integrating Apache Cassandra with Analytics Frameworks
To extract valuable insights, integrating Apache Cassandra with modern analytics frameworks is crucial:
Using Apache Spark
Data scientists and analysts can utilize Apache Spark to process data stored in Cassandra:
- Connect to Cassandra: Use the Apache Cassandra Connector for Spark.
- Execute Transformations: Perform transformations and actions on the RDDs (Resilient Distributed Datasets) loaded from Cassandra.
- Data Visualization: Load the processed data into BI tools or visualization frameworks such as Tableau or Power BI.
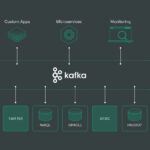
Using Apache Kafka
For streaming data ingestion, pairing Cassandra with Apache Kafka enables efficient handling of real-time data streams:
- Set Up Kafka Producers: Produce real-time events that Kafka will manage.
- Stream to Cassandra: Use Kafka Connect to transform and stream the data directly into Cassandra.
Real-Time Analytics Use Cases with Apache Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is versatile and can support various real-time analytics applications:
Fraud Detection in Financial Services
Financial institutions can utilize real-time analytics to monitor transactions for potential fraud. By ingesting event data continuously and applying ML algorithms over real-time data streams, banks can quickly spot anomalies.
IoT Data Processing
In the Internet of Things (IoT) space, data from devices can be ingested in real-time. Cassandra can store this telemetry data, allowing for real-time processing and analytics on large volumes of continually generated data.
Personalized Marketing Campaigns
Companies can analyze user behavior in real-time to tailor marketing campaigns effectively. By combining the data with machine learning models, organizations can predict user preferences and send customized promotions.
Best Practices for Using Apache Cassandra for Real-Time Analytics
To ensure optimal performance when using Cassandra for real-time data analytics, consider the following best practices:
- Design Data Structures Carefully: Create your tables with clustering keys that will optimize your read patterns.
- Monitor Performance: Utilize tools like Datastax OpsCenter to monitor cluster health and performance metrics.
- Scalable Architecture: Ensure your architecture can scale horizontally by adding additional nodes as required.
Challenges of Using Apache Cassandra
While Apache Cassandra is a powerful tool for real-time analytics, there are challenges to consider:
- Complexity of Management: Operating and maintaining a highly available Cassandra cluster can require significant expertise.
- Consistency Trade-offs: As a distributed system, achieving strong consistency can be challenging due to eventual consistency models.
- Learning Curve: For teams familiar with traditional relational databases, there might be a steep learning curve in understanding Cassandra’s architecture and CQL.
Conclusion
By leveraging the strengths of Apache Cassandra, organizations can effectively manage and analyze big data in real-time, driving insights and decision-making strategies. With proper implementation practices, Cassandra can serve as a robust backbone for various analytical needs.
Apache Cassandra offers a reliable and efficient solution for real-time data analytics in the realm of Big Data. By leveraging its distributed architecture, scalability, and fast read/write capabilities, organizations can handle large volumes of data and derive valuable insights in real-time. With its robust features and flexibility, Apache Cassandra stands out as a powerful tool for processing and analyzing data at scale, making it a top choice for tackling the challenges of Big Data analytics.