In a microservices architecture, implementing API service discovery is crucial for efficient communication and collaboration among various services. Service discovery enables services to dynamically locate and communicate with each other without prior knowledge of network or endpoint details. This is particularly important in a distributed system where services are constantly scaling up or down.
By leveraging service discovery mechanisms, such as a registry or a service mesh, APIs and web services within a microservices architecture can be easily discovered, registered, and managed. This helps in maintaining a highly available and resilient system by automatically routing traffic to healthy instances and enabling seamless integration of new services.
In this context, the implementation of API service discovery plays a pivotal role in promoting agility, scalability, and reliability within a microservices architecture. It simplifies the complexity of service interactions and enhances the overall performance and flexibility of the system.
In a microservices architecture, applications are composed of small, independently deployable services that communicate over a network. This architecture enhances the agility, scalability, and maintainability of applications. However, as the number of services increases, managing these services efficiently becomes challenging. This is where API Service Discovery plays a vital role.
Understanding API Service Discovery
API Service Discovery is a mechanism that allows services to locate and communicate with each other automatically. Instead of hardcoding the service locations (URLs) in the code, service discovery helps services find each other dynamically. This is crucial in a distributed system where services can come and go due to scaling needs or failures.
Types of Service Discovery
There are two primary types of service discovery:
- Client-Side Discovery: In this approach, the client is responsible for determining the network locations of available service instances. The client queries a service registry to obtain a list of service instances and then makes a request to one of those instances.
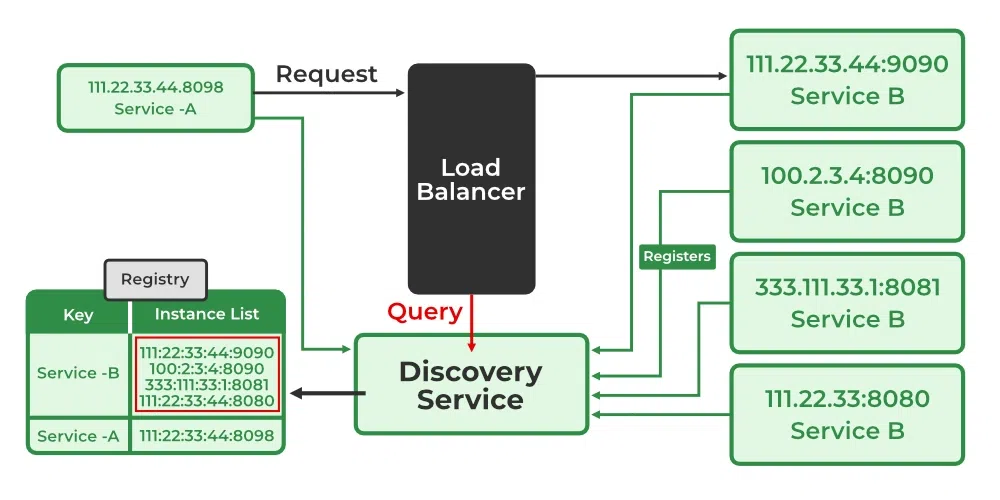
- Server-Side Discovery: In server-side discovery, the client makes a request to a load balancer or API gateway, which then queries the service registry and forwards the request to one of the available service instances. This offloads the discovery logic from the client to the server.
Implementing Service Discovery
To implement API Service Discovery in a microservices architecture, follow these comprehensive steps:
1. Choose a Service Discovery Tool
Select an appropriate service discovery mechanism. Popular tools include:
- Consul: Offers a service registry, health checking, and key-value storage.
- ZooKeeper: Provides a centralized service for maintaining configuration information, naming, and providing distributed synchronization.
- etcd: A distributed key-value store used for configuration management that is resilient and always available.
- Eureka: A REST-based service that is primarily used in Spring Cloud environments for service registration and discovery.
2. Register Services
Each service instance should register itself with the chosen service discovery tool. This often involves a simple HTTP call to register the instance along with metadata such as service name, port, and health check URL. For example, in Consul, a service can be registered via:
POST /v1/agent/service/register
{
"ID": "service1",
"Service": {
"Service": "my-service",
"Port": 8080,
"Tags": ["api", "v1"],
"Address": "127.0.0.1"
}
}
3. Implement Health Checks
Service health checks ensure that only healthy service instances are accessible. Both clients and service registries can perform these checks. For example, Consul allows configurable health checks that can be HTTP-based or TCP-based:
{
"Service": {
"Service": "my-service",
"Check": {
"http": "http://127.0.0.1:8080/health",
"interval": "10s"
}
}
}
4. Client-Side Discovery Implementation
In a client-side discovery setup, your client needs to query the service registry for available instances. This is typically done using a library or framework that abstracts the logic. In a Spring Boot application, for example, you can use Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka to handle the discovery:
@Autowired
private EurekaClient eurekaClient;
String serviceURL = eurekaClient.getNextServerFromEureka("SERVICE-NAME", false).getHomePageUrl();
5. Server-Side Discovery Implementation
If opting for a server-side discovery approach, implement the API gateway or load balancer to handle requests and forward them to the appropriate service. Tools like NGINX and Spring Cloud Gateway serve this purpose well. Basic NGINX configuration would look like:
http {
upstream my_service {
server service1:8080;
server service2:8080;
}
server {
location /my-service {
proxy_pass http://my_service;
}
}
}
6. Implement Circuit Breakers
To enhance the resilience of your microservices, it’s critical to implement circuit breakers. These can prevent service calls from overwhelming a service that is experiencing issues. Libraries like Hystrix or Resilience4j provide mechanisms to implement circuit breakers easily:
CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker = circuitBreakerRegistry.circuitBreaker("serviceName");
String response = circuitBreaker.executeSupplier(() -> {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://my-service", String.class);
});
Challenges in API Service Discovery
While implementing API service discovery improves microservices communication, it comes with challenges:
1. Network Latency
Service discovery can introduce latency due to the overhead of querying the registry. Optimize this by caching service locations on the client-side or at the API gateway level.
2. Complexity in Configuration
As the number of services grows, managing different configurations can become complex. Use templating tools like Helm or configuration management systems to streamline deployment.
3. Versioning and Compatibility
Version management between services becomes critical as updates occur. Implement standardized processes for versioning and use API gateways to manage backward compatibility.
Best Practices for Service Discovery
Implementing API Service Discovery effectively requires adherence to certain best practices:
- Secure the Service Registry: Use authorization and encryption mechanisms to protect service registration data.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor service health and the status of service discovery to quickly identify issues.
- Implement Logging and Tracing: Use distributed tracing tools like Jaeger or Zipkin to track requests across multiple services.
- Test for Resilience: Regularly perform chaos engineering practices to evaluate the reliability of service discovery under various failure scenarios.
Conclusion
Implementing API Service Discovery in microservices architecture is crucial for ensuring efficient communication and scalability. By understanding the various methods of service discovery and following best practices, you can build resilient and maintainable systems that can adapt to changing demands. As your microservices ecosystem grows, investing time in setting up a robust service discovery mechanism will pay dividends in terms of operational efficiency and service reliability.
Implementing API service discovery in a microservices architecture is crucial for effective communication and seamless integration between services. By utilizing service registries, load balancers, and API gateways, organizations can automate service discovery, enabling scalability, flexibility, and resilience within their API ecosystem. Embracing a service discovery approach fosters optimal performance, enhances reliability, and simplifies the management of APIs in a dynamic and distributed environment.