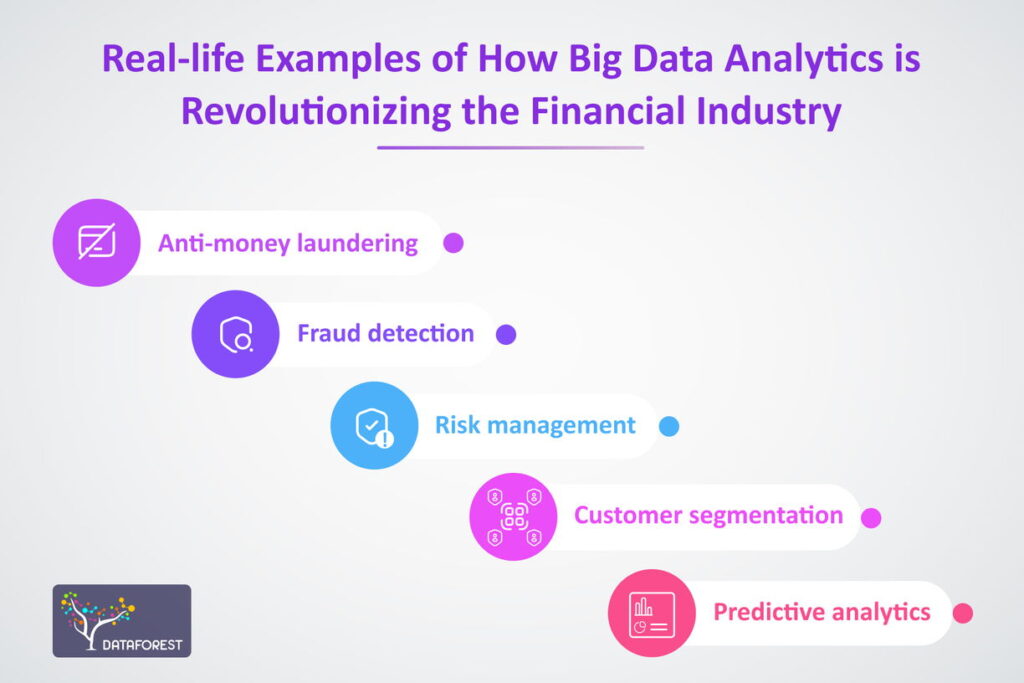
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the financial industry, Big Data has emerged as a game-changing force, revolutionizing the way organizations manage risk. Big Data refers to large volumes of structured and unstructured data that can be analyzed to reveal patterns, trends, and associations, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making. Within the financial sector, the utilization of Big Data analytics has become integral to risk management strategies, enabling institutions to identify, assess, and mitigate risks in a proactive and efficient manner. This article explores the critical role of Big Data in transforming risk management practices within the financial industry, highlighting its impact on decision-making, compliance, and overall operational resilience.
Understanding Big Data in Finance
In the contemporary financial landscape, Big Data has emerged as a transformative asset, enabling organizations to analyze vast amounts of information accurately and efficiently. The integration of Big Data analytics into the financial sector is not just a trend; it’s a necessity for effective risk management. Financial institutions such as banks, insurance firms, and investment companies harness data from various sources including transaction histories, social media, regulatory changes, and market trends.
Types of Risks in the Financial Sector
Within the financial industry, risk can manifest in several forms. Understanding these risks is crucial for implementing effective Big Data solutions. Some of the key types of risks include:
- Credit Risk: The possibility of a loss resulting from a borrower’s failure to repay a loan or meet contractual obligations.
- Market Risk: The risk of losses in the financial markets due to fluctuations in market prices.
- Operational Risk: This involves risks arising from internal processes, people, and systems or from external events.
- Liquidity Risk: The inability to meet short-term financial obligations due to an imbalance between assets and liabilities.
- Regulatory Risk: The risk of financial loss due to changes in laws and regulations.
The Role of Big Data in Risk Management
Big Data plays a pivotal role in enhancing risk management strategies through various methodologies:
1. Predictive Analytics
One of the most significant advantages of Big Data is its ability to facilitate predictive analytics. Financial institutions can utilize historical data sets to forecast future trends and behaviors. For instance, by analyzing past credit data, organizations can predict which clients are likely to default on loans, enabling proactive risk mitigation strategies.
2. Real-Time Data Processing
With the help of Big Data technologies, financial organizations can process and analyze data in real time. This capability allows for rapid responses to emerging risks. For example, if unusual trading patterns are detected, institutions can act quickly to prevent potential fraud or a market crash.
3. Enhanced Risk Assessment Models
Big Data enables the development of advanced risk assessment models that incorporate a broader range of variables than traditional methods. This includes qualitative data from news articles, social media sentiment, and economic indicators. By utilizing machine learning (ML) algorithms, financial institutions can refine their risk evaluation processes, leading to more accurate assessments.
4. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Fraud is an ever-present threat in the financial industry, and Big Data analytics can significantly enhance fraud detection efforts. By aggregating and analyzing diverse data sets, financial organizations can identify suspicious patterns that may indicate fraudulent activity. For instance, machine learning techniques can flag outlier transactions that deviate from established customer behavior, allowing for swift intervention.
5. Stress Testing
Big Data can substantially improve the efficiency and accuracy of financial stress testing — a crucial component of risk management. By simulating various market scenarios using Big Data tools, institutions can test their resilience under extreme conditions. This proactive approach enables them to pinpoint vulnerabilities and devise strategies to strengthen their financial stability.
Benefits of Implementing Big Data in Risk Management
The integration of Big Data in risk management is associated with several substantial benefits:
1. Improved Decision-Making
Data-driven decision-making empowers financial institutions by providing comprehensive insights. Business intelligence tools incorporating Big Data analytics can help executives make informed choices, thus minimizing exposure to risks.
2. Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
Staying compliant with financial regulations is critical. Using Big Data, firms can streamline their compliance processes by maintaining a comprehensive record of all transactions and communications. This facilitates easier audits and ensures adherence to regulatory standards.
3. Cost Reduction
While initial investments in Big Data technologies can be significant, the long-term cost savings are substantial. By implementing automated risk analysis and monitoring systems, financial organizations can reduce the labor costs associated with manual evaluations and minimize financial losses due to undetected risks.
4. Greater Customer Insights
Understanding customer behavior and preferences is essential for maintaining competitive advantage in the financial sector. Big Data analytics can provide valuable insights regarding customer needs, which can also help in personalizing financial products and services, thus improving customer loyalty and satisfaction.
5. Increased Efficiency
Automating data collection and analysis significantly improves operational efficiency. Financial institutions can save time and resources through the use of technology for routine tasks, allowing human analysts to focus on strategic planning and decision-making.
Challenges in Implementing Big Data Solutions
Despite the myriad benefits, financial institutions face several challenges when it comes to adopting Big Data technologies:
1. Data Privacy and Security
The handling of sensitive financial data raises significant concerns around privacy and security. Organizations must ensure their Big Data frameworks comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to safeguard customer information.
2. Data Quality and Integration
Ensuring data quality is paramount; poor-quality data can lead to erroneous insights and decision-making. Financial organizations often operate with data from multiple sources, which require integration into a coherent framework. This can be a complex task necessitating ongoing management and refinement.
3. Talent Shortage
There is a growing demand for skilled professionals who can interpret Big Data to inform risk management strategies. The shortage of qualified data scientists and analysts presents a challenge, hindering the effective implementation of Big Data initiatives.
4. Rapid Technological Changes
The landscape of Big Data technologies is constantly evolving. Financial institutions must stay abreast of new tools and techniques, which can be both resource-intensive and costly.
The Future of Big Data in Financial Risk Management
The future of Big Data integration in financial risk management looks promising, with several trends anticipated to shape the industry:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into Big Data analytics will further enhance risk management capabilities. These technologies can identify patterns more accurately and make predictions with higher precision, contributing to improved overall outcomes.
2. Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP), a branch of AI, will play an increasing role in analyzing unstructured data, such as news articles and social media. This will provide financial organizations with insights into market sentiment and its potential impact on risk.
3. Blockchain Technology
The adoption of blockchain technology in the financial sector can improve data security and transparency in transactions, further mitigating risks associated with fraud and data breaches.
4. Rising Importance of Ethical Data Use
As organizations increasingly focus on customer privacy, the ethical use of Big Data will become paramount. Establishing ethical frameworks for data usage will not only build trust but will also enhance compliance with regulations.
5. Integration of Internet of Things (IoT)
The combination of Big Data with IoT devices presents new opportunities for risk assessment. Real-time data streaming from IoT can assist financial institutions in monitoring factors that contribute to various types of risks, ensuring timely interventions.
The integration of Big Data in risk management processes within the financial industry has proven to be essential for enhancing decision-making processes, improving risk assessment, and driving more informed strategies. The utilization of advanced analytics and data-driven insights has enabled financial institutions to proactively identify and mitigate risks, achieve regulatory compliance, and ultimately enhance operational efficiency and profitability. Embracing Big Data technologies will continue to be a critical driver for competitive advantage and sustainable growth in the dynamic landscape of the financial sector.