Creating a high-availability Big Data architecture is crucial for businesses looking to efficiently manage and analyze large volumes of data. By implementing a robust infrastructure that ensures data is accessible and reliable at all times, organizations can enhance their decision-making process and drive innovation. In this guide, we will explore essential strategies and considerations for building a high-availability Big Data architecture that can support the scalability, reliability, and performance requirements of today’s data-driven world.
Understanding High Availability in Big Data
High availability (HA) in the context of big data architecture refers to the systems and configurations that create a robust environment for continuous operations, minimizing downtime during both planned and unplanned outages. Achieving HA involves implementing strategies that ensure data integrity, system reliability, and rapid recovery. The need for high availability arises from the demands of modern enterprises that rely heavily on data for decision-making.
Key Components of High-Availability Big Data Architecture
A well-designed high-availability big data architecture includes several key components:
- Redundant Systems: Utilizing multiple nodes and clusters to provide failover capabilities.
- Load Balancing: Distributing workloads evenly across various systems to avoid bottlenecks.
- Data Replication: Creating copies of data across different geographical locations to ensure accessibility.
- Automated Failover Mechanisms: Implementing automated systems to switch to backup resources seamlessly.
- Monitoring and Alerting: Utilizing tools for real-time monitoring and alerts to respond quickly to issues.
Choosing the Right Technologies
To build a high-availability big data architecture, selecting the appropriate technologies is crucial. Some of the popular frameworks and tools include:
1. Apache Hadoop
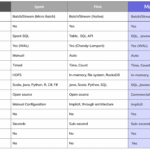
Apache Hadoop is a cornerstone of many big data architectures. Deploying Hadoop in a clustered setup with Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) provides a resilient framework capable of fault tolerance through its inherent data replication mechanisms. Each file is split into blocks that are replicated across multiple nodes, ensuring data availability even in the event of hardware failures.
2. Apache Spark
Apache Spark offers advanced analytics and can run up to 100 times faster than traditional big data technologies. To achieve high availability, you can set up Spark in a cluster mode, making use of mechanisms like resilient distributed datasets (RDDs) to manage failure by re-computing lost data.
3. NoSQL Databases
Choosing the right type of NoSQL database can significantly enhance the availability of a big data architecture. Databases such as Cassandra and MongoDB support built-in sharding and replication. These features distribute data across nodes and maintain copies, allowing for quick recovery during outages.
Designing the Architecture
When designing a high-availability big data architecture, consider the following best practices:
1. Multi-Node Clusters
Implementing a multi-node cluster entails configuring several nodes that can take over for each other seamlessly. Use cluster management tools like Apache ZooKeeper to manage distributed configurations, maintain system synchronization, and provide high availability for distributed systems.
2. Geographic Redundancy
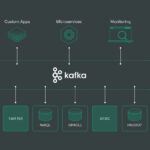
To protect against site-specific failures, consider a multi-region deployment. This means setting up clusters in separate geographic areas. Utilize data replication strategies to keep all copies synchronized. This can be done through tools like Apache Kafka for streaming data or with built-in capabilities of databases like Cassandra.
3. Configuration Management
Maintain consistency across your infrastructure by utilizing configuration management tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef. These tools help automate deployments and ensure that every node follows the same setup protocols, making recovery and fault tolerance easier.
Implementing Load Balancing
Load balancing improves the performance and responsiveness of your big data architecture. It spreads out workloads, reduces contention, and maximizes resource utilization. Here are a few techniques:
1. Use of Load Balancers
Implementing software load balancers such as Nginx or HAProxy helps distribute incoming requests across multiple nodes effectively. This approach assists in maintaining optimal performance and availability.
2. DNS Round-Robin
Another simple technique for load distribution is DNS round-robin, which allows multiple IP addresses for a single domain name. This setup enables clients to connect to different cluster nodes, reducing the load on any single node.
Implementing Failover Mechanisms
Automatic failover mechanisms are critical to maintaining high-availability in a big data architecture. Here’s how to implement them:
1. Heartbeat Monitoring
Use heartbeat signals to monitor the health of nodes. If a node fails to respond within a certain timeframe, the system should automatically redirect requests to a healthy node. Tools like Nagios and Prometheus help monitor clusters effectively.
2. Active-Active Configuration
Consider an active-active configuration, wherein multiple nodes process requests concurrently. This setup prevents single points of failure and allows continuous operations even during node outages.
Utilizing Backup and Restore Strategies
An integral part of a high-availability big data architecture is having solid backup and restore strategies.
1. Regular Backups
Schedule regular backups of your data to ensure recoverability. Tools like Apache NiFi can orchestrate complex data flows and help automate backup processes.
2. Testing Recovery Procedures
Regularly test your recovery processes to ensure they work as expected. Simulating failures and verifying your system’s ability to recover swiftly is crucial for confidence in your architecture.
Monitoring and Alerting Systems
Set up comprehensive monitoring and alerting systems to provide insights into the performance and health of your architecture. Consider these aspects:
1. Real-time Monitoring Solutions
Utilize tools such as Grafana and Elasticsearch to monitor system metrics and performance. Real-time insights into resource usage can often preemptively address issues before they cause downtime.
2. Alerts and Notification Systems
Configure alerting mechanisms that notify the appropriate teams upon detecting failures or performance degradation. Examples include sending alerts via Slack, email, or SMS to ensure quick response times.
Conclusion
Building a high-availability big data architecture requires careful planning and execution across various components and technologies. By implementing redundancy, data replication, load balancing, and robust monitoring, organizations can ensure their big data systems remain operational, efficient, and responsive to the needs of the business.
Building a high-availability Big Data architecture is essential for ensuring consistent access to data and efficient processing in the face of failures. By incorporating redundancy, scalability, and fault tolerance into the design, organizations can create a resilient infrastructure capable of meeting the demands of Big Data processing. Emphasizing proper data management practices and leveraging technologies such as distributed computing and data replication are key strategies in achieving a reliable and high-availability Big Data architecture.