Ensuring high availability is crucial for API and web service environments to maintain uninterrupted access to critical data and functionality. One effective approach to achieve this is by implementing API redundancy. API redundancy involves setting up multiple instances of the same API service across different servers or locations to ensure redundancy and fault tolerance. This strategy helps in distributing the incoming traffic load, mitigating downtime risks, and providing seamless user experiences. In this guide, we will explore best practices and considerations for implementing API redundancy to enhance the availability and reliability of your API and web service infrastructure.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring high availability for your APIs and web services is crucial to maintain user trust and satisfaction. API redundancy is a vital strategy that can minimize downtime and enhance reliability. This article will guide you through the steps to implement API redundancy effectively.
Understanding API Redundancy
API redundancy involves creating multiple instances of an API to ensure that even if one instance fails, others can take over. This strategy is essential for achieving high availability (HA) of your services. Here are the core concepts related to implementing API redundancy:
- Load Balancing: Distributing incoming traffic among multiple API instances to prevent any single instance from becoming overwhelmed.
- Failover Mechanisms: Automatic switching to a redundant or standby system in the event of a failure.
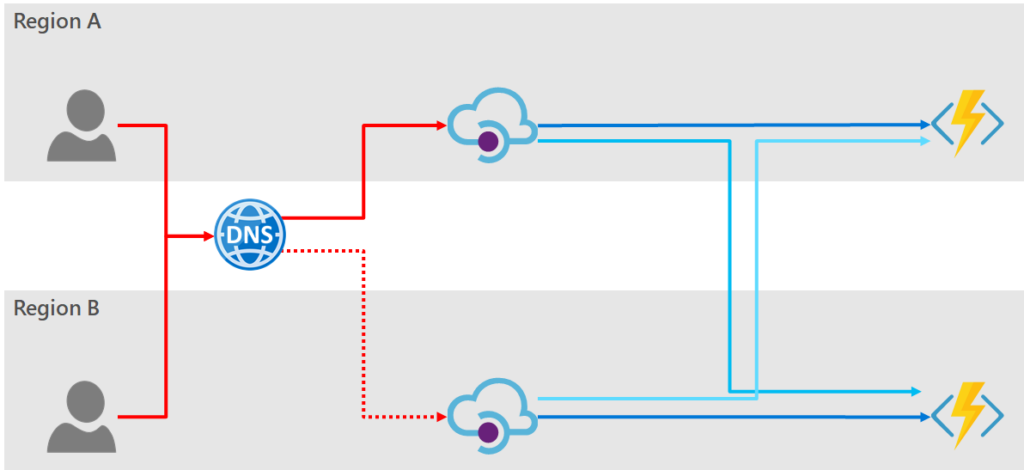
- Geographic Redundancy: Deploying API instances in multiple data centers located in different regions to prevent service disruption due to localized incidents.
Choosing the Right Architecture
The first step in implementing API redundancy is selecting an appropriate architecture. Below are some popular architectures that support high availability:
Microservices Architecture
In a microservices architecture, each service is independently deployable. This allows for easy replication of services and scaling based on demand. Microservices provide the flexibility to deploy redundant APIs quickly by spinning up additional service instances.
Serverless Architecture
Serverless architecture leverages cloud functions or managed services that run in response to events. In this model, redundancy is inherently managed by the cloud provider, automatically scaling the number of instances based on user requests and maintaining high availability.
Containerized Applications
Using containers (like Docker) enables you to create isolated environments for each API instance. Container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes can manage the deployment, scaling, and redundancy of your API containers, making it easy to achieve HA.
Implementing Load Balancing
Load balancing is vital for distributing traffic among various API instances. Here’s how to implement it:
Using Software Load Balancers
Software load balancers like Nginx or HAProxy can be set up to route requests to healthy API instances. They can intelligently route traffic based on various algorithms, such as round-robin, least connections, or IP hash. Set up health checks to remove instances that are not functioning properly.
Cloud Provider Load Balancers
Using cloud provider load balancers (such as AWS Elastic Load Balancing or Google Cloud Load Balancing) can simplify the process. These managed services automatically handle scalability, health checks, and security, allowing developers to focus on building features rather than managing infrastructure.
Implementing Failover Strategies
To ensure that your API remains available during failures, implementing robust failover strategies is vital. Here are key strategies to consider:
Active-Passive Failover
In an active-passive setup, one instance handles all the traffic while a standby instance is on standby. If the primary instance fails, the traffic is quickly redirected to the standby instance. Implement watchdog scripts to monitor the health of your APIs and trigger failover automatically.
Active-Active Failover
In an active-active configuration, multiple instances are processing requests concurrently. This setup not only provides redundancy but also enhances performance by spreading the load. API Gateway services can facilitate this by routing traffic based on instance health or performance metrics.
Monitoring and Alerts
Monitoring your APIs is crucial for identifying issues proactively. Implement the following monitoring strategies:
Use APM Tools
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools like New Relic, Dynatrace, or Datadog can provide insights into your API’s performance, error rates, and response times. Integrating these monitoring tools can help you quickly identify bottlenecks or instances that require failover.
Set Up Alerts
Configure alerts based on key performance indicators (KPIs). For instance, set thresholds for error rates, latency, and downtime. Utilize communication platforms like Slack or PagerDuty for instantaneous notifications when problems arise.
Testing for Redundancy
Testing your API redundancy is essential to ensure your implementation works as expected. Consider the following testing strategies:
Chaos Engineering
Practicing chaos engineering involves intentionally introducing failures into your system to test its resilience. Tools like Chaos Monkey can randomly terminate instances, verifying that your load balancer and failover mechanisms work seamlessly under stress.
Failover Drills
Conduct failover drills that simulate an instance failure. Measure response times and recovery efficiency to identify areas where improvement is needed. Regular drills can ensure your team is prepared for real-world incidents.
Implementing Geographic Redundancy
Geographic redundancy enhances availability by deploying API instances across multiple regions. Here’s how to achieve it:
Multi-Region Deployment
Deploy your APIs in multiple geographical locations, ensuring that users can access the nearest instance. For example, if you are using AWS, you can create API instances in different availability zones within multiple regions. Make sure to synchronize your databases and states between regions.
Global Traffic Management
Utilize Global Traffic Management (GTM) solutions to route users automatically to the closest healthy instance based on their location. Solutions like AWS Route 53 or Cloudflare can significantly enhance user experience while ensuring redundancy.
Security Considerations
When implementing API redundancy, security should be a priority. Consider the following measures:
API Keys and Tokens
Ensure all API instances are secured with API keys or tokens. Implement rate limiting across all instances to protect against abuse, especially in a scenario where failover may lead to increased load on backup services.
SSL/TLS Encryption
Use SSL/TLS encryption to protect data in transit between your clients and API instances. Ensuring secure communication is vital for maintaining user trust and adhering to compliance regulations.
Cost Considerations
While implementing API redundancy is essential for high availability, it is also vital to manage costs effectively:
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to assess the financial implications of redundancy strategies. Consider factors like increased operational costs, additional resource allocation, and potential revenue loss due to downtime.
Utilize Auto-Scaling
Employ auto-scaling features offered by cloud providers, which can dynamically adjust the number of running instances based on demand, ensuring you only pay for what you use during peak times while maintaining redundancy.
Documentation and Communication
Finally, ensure your API redundancy strategy is well-documented and communicated effectively across your team:
API Documentation
Update your API documentation to reflect redundancy strategies and configurations. This helps developers understand how to implement and troubleshoot redundancy features, fostering a culture of accountability and responsiveness.
Team Communication
Encourage continual communication about system performance and issues among team members. Regular meetings or updates can help ensure everyone is on the same page regarding API availability and redundancy efforts.
Implementing API redundancy for high availability in APIs and Web Services is crucial for ensuring continuity and reliability of operations. By creating duplicate instances of APIs across multiple servers or data centers, organizations can mitigate the risk of downtime and provide uninterrupted access to services for users. This redundancy strategy reinforces the resiliency of the system and minimizes the impact of potential failures, ultimately enhancing the overall performance and availability of the API infrastructure.