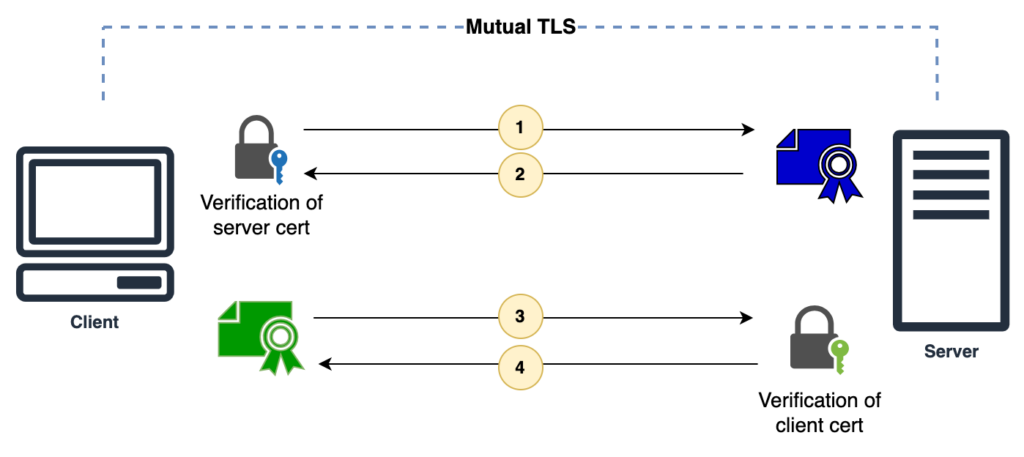
Implementing Mutual TLS Authentication in APIs is a crucial security measure for ensuring that communication between the client and server is secure and authenticated. Mutual TLS Authentication, also known as two-way TLS authentication, requires both the client and server to present valid certificates to authenticate each other. In the context of APIs and web services, this means that both the API client and the API server must exchange and validate certificates to establish a secure connection. This process helps prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and man-in-the-middle attacks, providing a robust layer of security for API communications. In this guide, we will explore the key steps and best practices for implementing Mutual TLS Authentication in APIs to enhance security and protect sensitive data.
Understanding Mutual TLS Authentication
Mutual TLS (mTLS) is an enhancement of the standard TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol, aiming to secure client-server communications by requiring both parties to authenticate themselves using cryptographic certificates. This adds a significant layer of security, particularly for APIs and web services, as it ensures that both the client and server are who they claim to be.
Why Use Mutual TLS in APIs?
The integration of mTLS in your API can offer several advantages:
- Enhanced Security: By requiring both client and server certificates, the chance of unauthorized access is reduced dramatically.
- Data Integrity: mTLS safeguards against data tampering, ensuring that data remains intact during transmission.
- Confidentiality: It ensures that only authenticated clients can access sensitive resources, bolstering privacy and security.
Prerequisites for Mutual TLS Implementation
Before diving into the implementation process, ensure you have the following in place:
- A web server set up to host your API (e.g., Apache, NGINX).
- A valid SSL/TLS certificate for your server.
- A client certificate signed by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
- A working knowledge of your server configuration files.
Setting Up a Certificate Authority (CA)
To properly implement mTLS, you’ll need a CA to issue and manage certificates. You can either rely on an external CA provider or set up your own using tools like OpenSSL. Here’s a general guide:
# Create the private key for the CA
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out ca-key.pem
# Create the CA certificate
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ca-key.pem -sha256 -days 1024 -out ca-cert.pem
This will generate a private key and a CA certificate that you can use to sign client certificates.
Generating and Signing Client Certificates
Follow these steps to create a client certificate that will be verified by your API:
# Generate a private key for the client
openssl genpkey -algorithm RSA -out client-key.pem
# Create a certificate signing request (CSR)
openssl req -new -key client-key.pem -out client-csr.pem
# Sign the client CSR with your CA
openssl x509 -req -in client-csr.pem -CA ca-cert.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -out client-cert.pem -days 365 -sha256
You now have a client certificate that you can use to establish secure communication with your API.
Configuring Your Web Server for Mutual TLS
Next, you need to configure your web server to support mTLS. Below are configurations for two popular web servers, Apache and NGINX.
Apache Configuration
For Apache, enable the necessary modules and configure your virtual host:
# Load required modules
LoadModule ssl_module modules/mod_ssl.so
ServerName your-api.example.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /path/to/your/server-cert.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /path/to/your/server-key.pem
SSLCACertificateFile /path/to/ca-cert.pem
SSLVerifyClient optional
SSLVerifyDepth 2
NGINX Configuration
For NGINX, add the following lines to your server block:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name your-api.example.com;
ssl_certificate /path/to/your/server-cert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/your/server-key.pem;
ssl_client_certificate /path/to/ca-cert.pem;
ssl_verify_client on; # Use 'off' for optional client verification
location /api {
proxy_pass http://backend_service; # Point to your backend service
}
}
Testing Mutual TLS Implementation
Once you’ve completed the server configuration, it’s essential to test the mTLS setup.
Using cURL for Testing
cURL is a powerful tool to test APIs. Use the following command to check if the mTLS is functioning:
curl -v -s --key client-key.pem --cert client-cert.pem https://your-api.example.com/api
You should receive a successful response if the configuration is set up correctly. If not, check your logs and configurations for any issues.
Handling Common mTLS Challenges
Despite the robust security benefits of mTLS, you may encounter challenges. Here’s how to address some common issues:
1. Client Certificate Not Recognized
This might be due to an untrusted CA. Ensure your CA certificate is properly configured on the server and that the client certificate is signed by this CA.
2. Connection Errors
Inspect your network configuration and firewall settings. Ensure that the necessary ports (e.g., port 443 for HTTPS) are open and reachable.
3. Performance Implications
mTLS introduces additional overhead due to the certificate checks. To mitigate performance issues, consider optimizing your server or using caching techniques where possible.
Best Practices for Implementing Mutual TLS
Adhering to best practices can help maintain the effectiveness of mTLS:
- Regular Certificate Rotation: Regularly rotate your server and client certificates to maintain security integrity.
- Logging and Monitoring: Implement logging for audit trails and to monitor unauthorized access attempts.
- Client Certificate Revocation: Maintain a revocation list for client certificates, using mechanisms like CRL (Certificate Revocation List) or OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol).
- Security Updates: Regularly update your server software and libraries to protect against vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
By implementing Mutual TLS authentication in your APIs, you can significantly enhance the security of your application. Understanding the foundational elements, addressing common challenges, and adhering to best practices will ensure a robust secure API ecosystem.
Implementing Mutual TLS Authentication in APIs is a crucial security measure to ensure that both the client and the server can authenticate each other’s identity using digital certificates. This adds an extra layer of protection to API endpoints, safeguarding against malicious activities and unauthorized access. By following best practices and adopting Mutual TLS Authentication, organizations can enhance the security posture of their APIs and provide a more secure environment for transmitting data over the web.