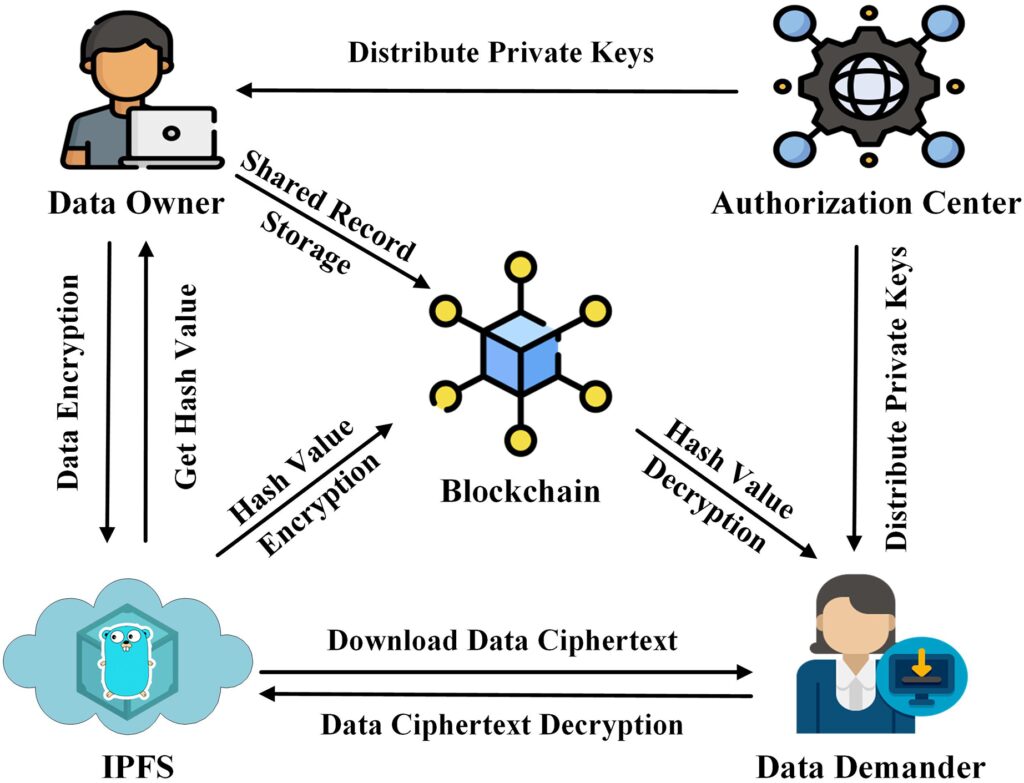
In the realm of Big Data, the need for secure and reliable data sharing mechanisms is ever-present. One transformative solution that has garnered attention in recent years is leveraging blockchain technology to implement secure data sharing practices. Blockchain, with its inherent characteristics of immutability, transparency, and decentralization, offers a promising framework for ensuring the integrity and privacy of data in Big Data environments. By integrating blockchain into Big Data systems, organizations can establish trust among multiple parties, facilitate secure and auditable data transactions, and overcome traditional challenges related to data sharing, such as data silos and concerns over data ownership. This article explores how integrating blockchain technology can revolutionize secure data sharing in the context of Big Data, paving the way for enhanced data integrity, confidentiality, and collaboration across diverse data sources and stakeholders.
The Importance of Secure Data Sharing in Big Data
In an age where organizations generate and depend on vast amounts of data, the need for secure data sharing has never been more critical. As businesses collect data from multiple sources, ensuring that the information remains accessible yet secure poses significant challenges. Data breaches can lead to monumental losses, making it imperative for companies to explore innovative solutions to safeguard their data.
Enter blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger system that provides a transparent and secure framework for data sharing. By leveraging the principles of blockchain, organizations can create a robust architecture for secure data sharing in Big Data environments.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
At its core, blockchain is a chain of blocks that securely store data using cryptography. Each block contains a list of transactions, a timestamp, and a link to the previous block, ensuring data integrity and chronological record keeping. Here are key features that make blockchain a preferred choice for big data security:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases hosted on single servers, blockchain stores data across a network of nodes, eliminating single points of failure.
- Immutability: Once a block has been added to the chain, it cannot be altered without consensus from the majority of the network, safeguarding against unauthorized changes.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to participants on the network, fostering trust among data-sharing parties.
- Privacy: Using advanced cryptographic algorithms, sensitive data can be shared without revealing the underpinning details.
Steps to Implement Secure Data Sharing Using Blockchain
1. Identify Use Cases for Secure Data Sharing
Determining the right use cases is essential to maximize the utility of blockchain in big data security. Common applications include:
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking products from origin to consumer ensures transparency and reduces fraud.
- Healthcare: Securely sharing patient data while preserving confidentiality enhances care coordination.
- Finance: Facilitating peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries reduces costs and accelerates processing times.
2. Choose the Right Blockchain Framework
Several blockchain platforms cater to different requirements. Popular frameworks include:
- Ethereum: Known for its smart contract capabilities, it supports numerous DApps (decentralized applications).
- Hyperledger Fabric: A permissioned blockchain ideal for enterprise solutions, allowing for controlled data access.
- Corda: Primarily developed for financial services, it enables businesses to manage complex transactions securely.
Selecting the appropriate blockchain framework is critical based on your organization’s specific data sharing needs and compliance requirements.
3. Implement Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These automated contracts enable seamless and secure transactions on the blockchain. For big data applications, smart contracts can help enforce data sharing rules, such as:
- Access controls that determine who can view or edit data.
- Automated payment systems that ensure value exchange whenever data is accessed or used.
- Data validation processes to ensure the integrity and authenticity of shared data.
4. Develop a Data Security Protocol
Creating a comprehensive data security protocol is crucial for leveraging blockchain technology effectively. This protocol should encompass:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data before adding it to the blockchain, securing it from unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based access controls to restrict data visibility based on user roles.
- Data Auditing: Establish auditing mechanisms to track data access and modifications for compliance and security review.
5. Enable Interoperability with Existing Systems
To fully exploit the potential of blockchain, it is vital to ensure its interoperability with existing systems. This process involves:
- Identifying data sources and determining how they can integrate with blockchain.
- Using APIs to facilitate seamless communication between blockchain applications and traditional systems.
- Implementing middleware solutions to bridge the gap between blockchain and existing databases.
6. Collaborate with Stakeholders
Collaboration among stakeholders is essential for successful implementation. Engage with:
- Data Providers: Ensure prerequisites for data sharing and establish trust in the system.
- End Users: Gather insights into user requirements and security expectations.
- Regulatory Bodies: Consult legal experts to navigate compliance regulations surrounding data sharing.
7. Monitor and Optimize the Blockchain System
After implementation, continuous monitoring is necessary to ensure the system meets its objectives. This phase can involve:
- Regular performance audits to identify bottlenecks or areas for improvement.
- Feedback loops from users to discover potential issues and enhance user experience.
- Adjustment of security measures as new threats emerge within the cybersecurity landscape.
Benefits of Using Blockchain for Secure Data Sharing
Incorporating blockchain into big data management brings numerous advantages, such as:
- Enhanced Security: Protects data from unauthorized access and attacks via cryptographic measures.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlines processes by reducing intermediaries in data sharing transactions.
- Improved Trust: Transparency within the blockchain fosters trust among participants can lead to stronger collaborations.
Challenges to Consider
While blockchain offers numerous benefits, implementing it for secure data sharing also presents challenges:
- Scalability: As data volume increases, ensuring that the blockchain can handle large amounts effectively is paramount.
- Integration Complexity: Merging blockchain with existing systems can be technically challenging and resource-intensive.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating data privacy laws and regulations, especially in industries like finance and healthcare, can be intricate.
Future of Blockchain in Big Data
The combination of blockchain and big data represents a promising evolution in data management. As organizations increasingly adopt decentralized solutions, we can expect:
- Enhanced data ownership, where individuals or organizations control their data more securely.
- Innovative models for data monetization, allowing users to derive value from their data while maintaining privacy.
- The emergence of decentralized applications (DApps) in various sectors, further enhancing the ecosystem of secure data sharing.
Implementing secure data sharing with blockchain technology is a promising solution to address the challenges of data security and privacy in the context of Big Data. By leveraging the immutability and transparency of blockchain, organizations can ensure trust, integrity, and accountability in sharing sensitive information. This innovative approach holds great potential for enhancing data protection, facilitating secure collaboration, and driving value creation in the Big Data ecosystem.