Securing API endpoints is crucial when developing APIs and web services to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. One common method used to enhance security is by implementing API keys and HMAC (Hash-Based Message Authentication Code) authentication. API keys serve as unique identifiers for clients to access APIs, while HMAC authentication ensures message integrity and origin authenticity. By combining these two methods, developers can establish a more robust security layer for their API endpoints, allowing for secure data transmission and safeguarding against potential threats such as malicious attacks and unauthorized usage.
The security of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) is crucial in today’s digital landscape, where data breaches are increasingly common. API security involves various strategies, and two of the most prevalent methods are using API keys and HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) authentication. This article will guide you through the processes of implementing these techniques to safeguard your API endpoints.
Understanding API Keys
API keys are unique identifiers given to developers and applications that enable access to a specific API. They serve as a simple means of authentication to track and control how the API is consumed. Here are some key aspects of API keys:
- Unique Identification: Each API key is unique to a particular user/application combination.
- Access Control: APIs can restrict access based on the user’s API key, allowing for control over who can use the service.
- Rate Limiting: API keys can help enforce usage limitations, preventing abuse of the API.
How to Implement API Keys
To implement API key authentication, you need to follow these steps:
1. Generate an API Key
When a user registers for access, generate a unique API key. This key can be created using a secure random function or library. Store the API key securely in your database, linking it to the user account.
2. Validate API Key on Requests
For every incoming request to your API, you need to validate the provided API key:
if request.api_key not in stored_api_keys:
return "Unauthorized", 401Make sure to check against your database or another secure storage mechanism to validate the key. Return an unauthorized status code if the key is invalid.
3. Monitor API Key Usage
Track the usage of API keys to identify any potential misuse. Monitoring can include:
- Counting the number of requests per key.
- Logging access details for audit trails.
- Implementing throttling mechanisms to limit excessive usage.
4. Rotate API Keys Regularly
To enhance security, regularly rotate your API keys. This involves:
- Generating a new API key for users and applications.
- Updating the system to use the new key while allowing older keys a grace period before deprecation.
5. Secure API Keys
Always ensure that API keys are not exposed in client-side code, repositories, or error messages. Keep them secured to prevent unauthorized use.
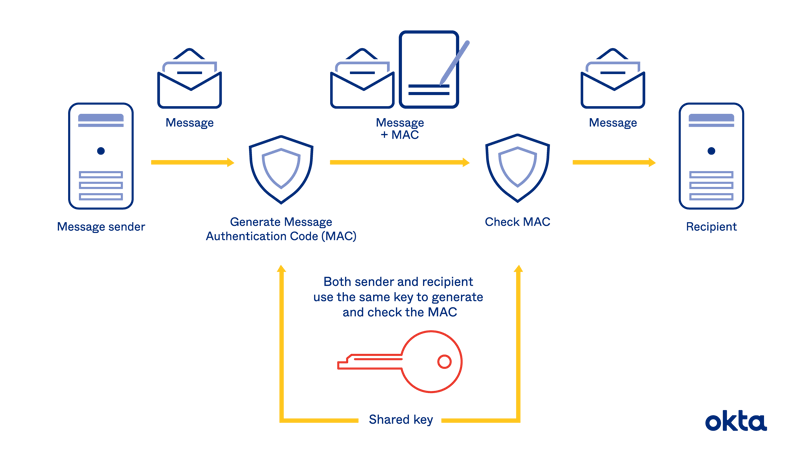
Understanding HMAC Authentication
HMAC authentication is a more advanced and secure method for verifying the integrity and authenticity of a message. Unlike simple API keys, HMAC involves a combination of a secret key and the message content:
- Secret Key: A shared secret known only to the client and API server.
- Message Content: Data being sent, including the request parameters and body.
How to Implement HMAC Authentication
HMAC authentication typically follows these steps:
1. Generate an HMAC Signature
When making a request, the client computes an HMAC signature of the request using the secret key and the request data:
import hashlib
import hmac
def create_signature(secret_key, data):
return hmac.new(secret_key.encode(), data.encode(), hashlib.sha256).hexdigest()2. Include the Signature in the Request
Add the computed HMAC signature as a header in the HTTP request:
headers = {
'X-Signature': create_signature(secret_key, request_data)
}3. Verify the HMAC Signature on the Server
On the server side, you need to extract the signature from the headers and validate it:
def verify_signature(received_signature, secret_key, data):
expected_signature = create_signature(secret_key, data)
return hmac.compare_digest(received_signature, expected_signature)
if not verify_signature(received_signature, secret_key, request_data):
return "Unauthorized", 4014. Use Timestamp and Nonce
To further enhance security, include a timestamp and a nonce in the request. This practice helps mitigate replay attacks:
- Timestamp: Indicates when the request was made; can prevent old requests from being accepted.
- Nonce: A unique identifier for each request, ensuring that no two requests have the same value.
5. Validate Time Difference and Nonce
On the server, check that the current time is within an acceptable range of the request timestamp and that the nonce wasn’t used on a previous request:
if abs(current_time - request_timestamp) > ALLOWED_TIME_DIFFERENCE:
return "Request expired", 403
if nonce_already_used(nonce):
return "Duplicate request", 403Best Practices for API Security
In addition to using API keys and HMAC authentication, consider the following best practices:
- Use HTTPS: Always communicate using HTTPS to encrypt data in transit and protect against man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Implement IP Whitelisting: Restrict access to your APIs to known IP addresses whenever possible.
- Provide Detailed Documentation: Include clear guidelines on how developers should use API keys and HMAC authentication, including best practices.
- Monitor and Audit: Regularly audit and monitor API usage to identify anomalies or unauthorized access attempts.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control: Different users may have different levels of access; ensure your APIs enforce these limitations.
Conclusion
By utilizing both API keys and HMAC authentication, you can greatly enhance the security of your API endpoints. While API keys offer a straightforward way to manage access, HMAC adds an important layer of data integrity and authenticity. Implementing these methods alongside best practices will help safeguard your APIs against unauthorized access and abuse.
Securing API endpoints using API keys and HMAC authentication is essential for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of API interactions. API keys help authenticate clients, while HMAC authentication ensures the confidentiality and integrity of data through message integrity checks. By implementing both methods, organizations can enhance the security of their API endpoints and protect against unauthorized access and data tampering, ultimately fostering trust with users and preventing potential security breaches.