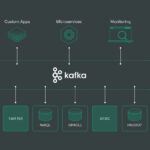
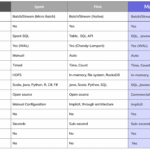
In the realm of Big Data analytics, Apache Kudu stands out as a powerful and efficient tool that enables organizations to accelerate their data processing and analysis. By seamlessly integrating with popular Big Data frameworks like Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark, Apache Kudu provides a high-performance and real-time storage solution for structured data. In this article, we will explore how to leverage Apache Kudu for fast analytics on Big Data, highlighting its key features and benefits in enhancing data processing speed and efficiency. Let’s delve deeper into the world of Apache Kudu and discover how it can revolutionize Big Data analytics.
What is Apache Kudu?
Apache Kudu is an open-source storage engine for big data that is designed to support fast analytics on large datasets. Unlike traditional databases, Kudu allows for efficient random access to data while maintaining low-latency and high-throughput capabilities. Its unique architecture makes it an ideal choice for interactive analytics and real-time data processing.
Key Features of Apache Kudu
- Columnar Storage: Kudu stores data in a columnar format, which allows for efficient compression and quick retrieval of specific columns, thereby speeding up analytics queries.
- ACID Transactions: Kudu supports ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions, ensuring data integrity while enabling concurrent read and write operations.
- Integration with the Hadoop Ecosystem: Kudu integrates seamlessly with popular components of the Hadoop ecosystem, like Apache Spark, Apache Impala, and Apache Hive, for enhanced analytical capabilities.
- Schema Evolution: The ability to alter schemas without downtime makes it flexible for big data applications that require frequent updates to data models.
Setting Up Apache Kudu
To use Apache Kudu effectively, you need to set it up in your big data environment. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Install Apache Kudu
- Download the latest version of Kudu from the official website.
- Install Kudu by following the installation guide, which includes steps for dependencies and environment settings.
- Ensure Java and other prerequisites are installed on your system.
Step 2: Configure Kudu
After installation, configure Kudu by adjusting the kudu-master and kudu-tserver settings in the respective configuration files. Key configurations include:
# In kudu-master:
--fs_wal_dir=/path/to/wal
--fs_data_dir=/path/to/data
# In kudu-tserver:
--fs_data_dir=/path/to/tserver-data
Step 3: Start Kudu Services
Run the following commands to start the Kudu master and tablet server:
kudu master start
kudu tserver start
Data Modeling in Apache Kudu
When using Apache Kudu for analytics, it is essential to design your data model effectively:
Choosing the Right Primary Key
The primary key in Kudu should be chosen based on the access pattern of your queries. It determines how the data will be distributed across tablet servers. Consider the time series or hash-based sharding methods for optimal performance.
Defining Column Types
Apache Kudu supports various data types such as INTEGER, STRING, DOUBLE, and BOOLEAN. Choose appropriate column types according to your data to optimize space and performance.
Using Partitions Wisely
Data can be partitioned based on specific criteria to enhance query performance. Effective partitioning allows queries to skip irrelevant data, enhancing overall throughput and reducing response times.
Loading Data into Apache Kudu
Data can be loaded into Kudu using various methods:
Using Impala
With Impala, you can easily connect to Kudu and load data. Execute the following SQL commands:
CREATE TABLE my_table (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name STRING,
value DOUBLE
) STORED AS KUDU;
INSERT INTO my_table VALUES (1, 'example', 10.0);
Using Kudu Command-Line Tools
Kudu provides several command-line tools for loading and managing data. Use kudu cluster for cluster operations and kudu table for table-level operations.
Querying Data in Apache Kudu
Once the data is loaded into Apache Kudu, you can perform analytics using various query mechanisms:
Using Apache Impala
Impala provides an efficient way to run SQL queries on Kudu tables:
SELECT * FROM my_table WHERE value > 5.0;
This interaction allows for low-latency queries that are optimized for data stored within Kudu.
Using Apache Spark
Apache Spark can easily connect to Kudu for both batch and streaming analytics. Use the following code to read data from Kudu:
val df = spark.read
.format("kudu")
.option("kudu.master", "localhost:7051")
.option("kudu.table", "my_table")
.load()
df.show()
Integrating Apache Kudu with Other Technologies
Apache Kudu’s seamless integration with other big data technologies enhances its utilization:
Apache Spark
With Kudu, you can leverage the massive processing capabilities of Spark for real-time analytics. Utilizing the Spark-Kudu connector enables efficient data manipulation and computation:
df.write
.format("kudu")
.option("kudu.master", "localhost:7051")
.option("kudu.table", "my_table")
.mode("append")
.save()
Apache Hive
Using Apache Hive with Kudu enables SQL-like query capabilities. Kudu tables can be created, managed, and queried directly from Hive:
CREATE TABLE my_hive_table (
id INT,
name STRING,
value DOUBLE
) STORED AS KUDU;
Performance Optimization in Apache Kudu
To maximize the performance of your Apache Kudu analytics, consider these optimizations:
Compression Techniques
Kudu supports various compression algorithms. Choose the right compression type (such as Snappy or LZ4) for your use case to strike a balance between performance and storage efficiency.
Replication and Fault Tolerance
Ensure high availability and data durability by configuring replication settings. Kudu allows setting replication factors for tablets, providing fault tolerance against server failures.
Monitoring and Tuning
Regularly monitor Kudu performance using built-in metrics and dashboards. Use these insights to tune configurations, ensuring optimal operations.
Real-World Use Cases of Apache Kudu
Apache Kudu is used across various industries for different applications:
IoT Data Analytics
Organizations leverage Kudu for real-time analytics on IoT sensor data, allowing for timely insights and action.
Financial Services
In finance, Kudu enables quick analysis of transactional data, helping in fraud detection and risk assessment.
Retail Analytics
Retailers utilize Kudu to process vast amounts of customer behavior data for personalized marketing strategies and inventory management.
Best Practices for Using Apache Kudu
- Always design your schema based on your query patterns to ensure efficient data retrieval.
- Leverage batch writes whenever possible to reduce the overhead of individual transactions.
- Regularly assess your partitioning strategy based on query performance metrics.
- Implement data retention policies to ensure that old and unused data doesn’t bloat your system.
Apache Kudu offers a powerful solution for enabling fast analytics on Big Data by efficiently combining storage and compute capabilities. Its unique architecture and features make it well-suited for real-time analytics use cases, providing high performance and low latency query processing. By leveraging Apache Kudu, organizations can unlock the full potential of their Big Data environments and derive valuable insights faster than ever before.