Cloud Spanner is a powerful and innovative solution for distributed big data storage, offering scalability, reliability, and global consistency for handling massive amounts of data. It provides a fully managed, horizontally scalable, and strongly consistent database service that seamlessly integrates with big data workflows. In this article, we will explore how to leverage Cloud Spanner to effectively store and manage large volumes of data in a distributed environment, enabling organizations to unlock valuable insights and drive data-driven decision-making processes.
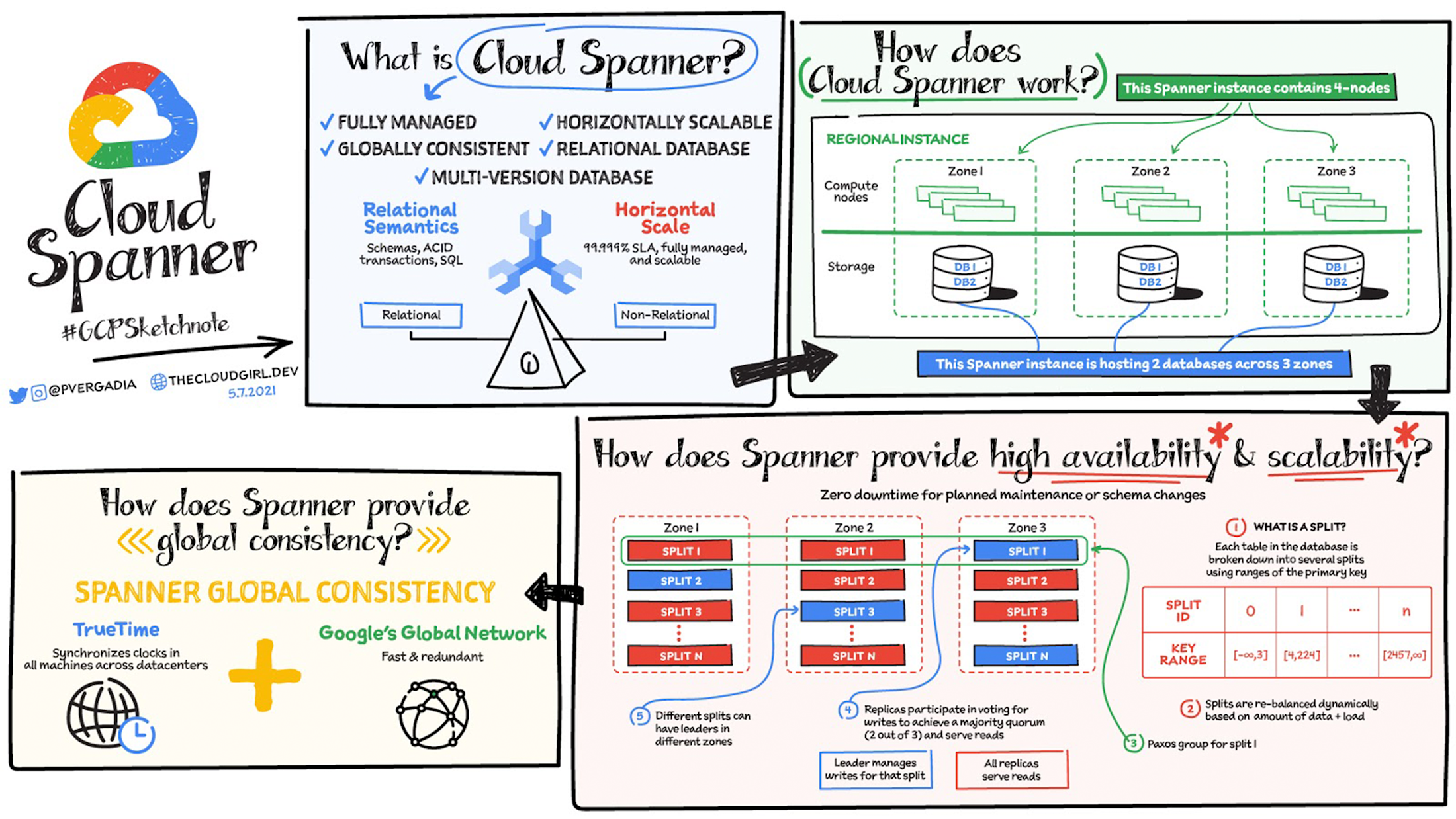
What is Cloud Spanner?
Cloud Spanner is a fully managed, scalable, globally-distributed database service offered by Google Cloud. It combines the benefits of relational databases, such as strong consistency and SQL support, with the scalability and performance of NoSQL systems. This makes Cloud Spanner an excellent choice for enterprises looking to manage big data in a reliable and efficient manner.
Key Features of Cloud Spanner
Here are some of the standout features that make Cloud Spanner suitable for distributed big data storage:
- Global Distribution: Data is automatically distributed across multiple regions, providing low-latency access to users worldwide.
- Horizontal Scalability: With the ability to scale out seamlessly, Cloud Spanner can handle increasing workloads without performance degradation.
- ACID Transactions: Supports multi-row and multi-table transactions, ensuring data integrity.
- Strong Consistency: Provides strong consistency with synchronous replication, which is critical for mission-critical applications.
- SQL Support: Offers a powerful SQL dialect that enables complex queries and data manipulation.
Getting Started with Cloud Spanner
Setting Up Your Cloud Spanner Instance
To utilize Cloud Spanner for your big data requirements, follow these steps to set up your instance:
- Create a Google Cloud Project: Ensure that you have an active Google Cloud project. If you don’t have one, create it in the Google Cloud Console.
- Enable the Cloud Spanner API: Navigate to the API & Services dashboard and enable the Cloud Spanner API.
- Create a Spanner Instance: In the Cloud Console, go to the Spanner section and click on “Create Instance.” Choose the configuration style, such as regional or multi-regional, based on your data needs.
- Set Up Your Database: After creating your instance, you can create a new database within it. Choose the appropriate schema and tables that reflect your data architecture.
Designing Your Schema
The design of your database schema is critical in optimizing performance and ensuring efficient data storage in Cloud Spanner. Consider the following guidelines:
- Use Interleaved Tables: Interleaved tables allow you to group related data together, which can improve query performance and reduce costs by optimizing storage.
- Design for Query Patterns: Anticipate the types of queries your application will perform and design your tables accordingly.
- Primary Keys: Choose primary keys wisely, ensuring they are unique and distribute your data evenly across the database.
Loading Data into Cloud Spanner
Once your database schema is set up, you can load data into Cloud Spanner:
Using the Cloud Spanner Client Libraries
Google provides various client libraries for popular programming languages such as Python, Java, Go, and Node.js. Here is how you can load data using Python:
from google.cloud import spanner
# Initialize Spanner client
spanner_client = spanner.Client()
instance = spanner_client.instance('your-instance-id')
database = instance.database('your-database-id')
def insert_data():
with database.batch() as batch:
batch.insert(
table='your-table-name',
columns=('id', 'name'),
values=[
(1, 'John Doe'),
(2, 'Jane Smith')
]
)
insert_data()
Using Data Import/Export Tools
You can also use the Data Transfer Service to import data from various sources, such as Google Cloud Storage or BigQuery, directly into Cloud Spanner.
Querying Data in Cloud Spanner
Understanding SQL Syntax in Cloud Spanner
Cloud Spanner supports a SQL dialect that includes standard SQL features like SELECT, JOIN, and GROUP BY. Here is an example of a simple query:
SELECT name
FROM your-table-name
WHERE id = 1
This will return the name associated with the specified ID. Complex queries can also be formed using JOIN to retrieve data from related tables.
Optimizing Queries for Performance
For large datasets, it’s essential to optimize your queries to avoid performance bottlenecks. Some best practices include:
- Limit Data Transfer: Use SELECT queries with WHERE clauses to minimize the amount of data being transferred.
- Utilize Indexes: Create indexes on columns that are frequently queried to speed up retrieval times.
- Batch Operations: Whenever possible, use batch processing for multiple data operations.
Monitoring and Managing Performance
To ensure that your Cloud Spanner instance is running efficiently, you can utilize Google Cloud’s built-in monitoring tools:
Using Stackdriver Monitoring
Google Cloud’s Stackdriver provides performance monitoring, logging, and diagnostics. Set up alerts to notify you of performance issues or SLA violations.
Resource Management
Manage your resources judiciously by adjusting the node count based on usage patterns. This can help reduce costs significantly while maintaining performance.
Security and Compliance
Data Encryption
Cloud Spanner automatically encrypts data at rest and in transit, ensuring your data is secure. However, for added layers of security, consider utilizing Google Cloud IAM to manage access permissions effectively.
Compliance Standards
Google Cloud Spanner complies with various global regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and others. Make sure to review your data practices to ensure compliance with the regulatory frameworks applicable to your industry.
Best Practices for Using Cloud Spanner with Big Data
To maximize the benefits of using Cloud Spanner for big data storage, consider the following best practices:
- Regular Data Maintenance: Regularly evaluate and clean your data to maintain optimal performance.
- Monitor Costs: Keep an eye on your spending to adjust resources as needed.
- Leverage Multi-Region Deployments: For critical applications, using multi-region deployments can enhance availability and reliability.
Integrating Cloud Spanner with Big Data Tools
Cloud Spanner can easily integrate with other Big Data tools and platforms. For instance:
- Apache Beam: Use Apache Beam for data processing and batch processing jobs in conjunction with Cloud Spanner.
- BigQuery: Transfer data from Cloud Spanner to BigQuery for advanced analytics and reporting capabilities.
- Dataflow: Implement Google Dataflow for stream and batch data processing with low latency.
Cloud Spanner offers a powerful and scalable solution for distributed big data storage in the cloud. By leveraging its globally-distributed database architecture and strong consistency guarantees, organizations can effectively manage large volumes of data while ensuring high availability and performance. Incorporating Cloud Spanner into a big data ecosystem can facilitate efficient data processing and analytics, making it a valuable asset for enterprises seeking to harness the full potential of their data assets.