In the fast-evolving landscape of big data, where vast amounts of sensitive information are processed and stored, the importance of implementing robust security measures cannot be overstated. Zero-trust security models have emerged as a critical framework for safeguarding big data environments against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. By assuming that every user and device within the network is a potential threat, the zero-trust approach ensures that access controls are consistently verified and validated, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. This paradigm shift in security strategy aligns perfectly with the dynamic and complex nature of big data, where traditional perimeter-based defenses are no longer sufficient to protect valuable datasets. Embracing zero-trust principles empowers organizations to secure their big data assets and maintain trust in the integrity and confidentiality of their data, ultimately fostering a safer and more resilient data ecosystem.
In the age of Big Data, the traditional security models are proving insufficient to combat the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. As businesses increasingly rely on vast datasets, they must explore more robust security frameworks. One of the most effective frameworks gaining traction is the Zero-Trust Security Model. This approach fundamentally alters the way organizations manage user access and data integrity.
Understanding Zero-Trust Security
The Zero-Trust Security Model operates on the principle that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organizational perimeter. This paradigm shift addresses numerous vulnerabilities inherent in conventional security practices, particularly in a Big Data context where large volumes of information can be susceptible to breaches.
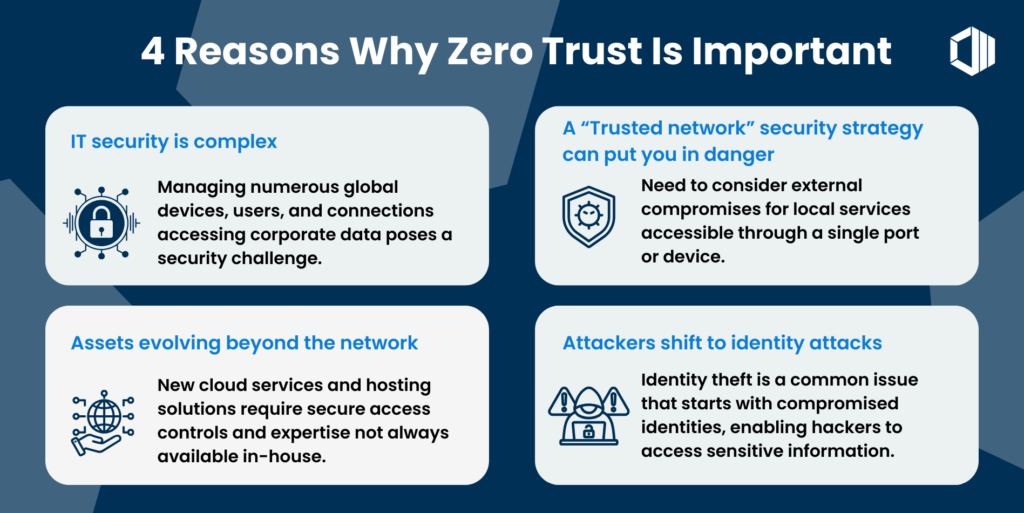
The Relevance of Zero-Trust in Big Data
As organizations accumulate ever-growing datasets, the need for stringent security measures becomes imperative. With the zero-trust model, organizations can enhance their data protection strategies significantly. Here are some key reasons why this model is crucial for Big Data:
1. Protecting Sensitive Data
In Big Data environments, sensitive information, including customer records and proprietary analytics, is constantly at risk. The zero-trust model ensures that access to this data is limited to authenticated and authorized users only. This minimizes the risk of data breaches, which can have catastrophic ramifications for businesses.
2. Decreasing the Attack Surface
With a traditional security model, once a user gains access to the network, they often have excessive privileges that allow them to traverse the system. However, the zero-trust approach drastically reduces the attack surface by enforcing strict access controls. Only authenticated users can access specific datasets, significantly reducing the potential entry points for malicious actors.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Validation
Effective security is not just about initial access but also about continuous monitoring of user behavior. The zero-trust model advocates for ongoing validation of user identity and access rights. This is particularly essential in Big Data environments, where real-time data processing necessitates that security measures adapt dynamically as users access different datasets.
Implementing Zero-Trust Security in Big Data
To effectively implement a zero-trust security model in a Big Data environment, organizations should consider the following steps:
1. Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. This limits access to data resources based on user role, thereby minimizing potential damage if a breach occurs. In the context of Big Data, micro-segmentation helps protect sensitive datasets, ensuring that only authorized personnel or systems can interact with them.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Establishing a robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) system is fundamental to the zero-trust model. Utilizing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO) can help reinforce access controls. Moreover, IAM solutions tailored for Big Data can provide fine-grained permissions, ensuring that users can only access the data necessary for their roles.
3. Data Encryption
Data must be encrypted both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they cannot interpret it without the appropriate decryption keys. Implementing strong encryption protocols is a crucial aspect of protecting sensitive Big Data assets.
4. Behavior Analytics
Behavioral analytics tools can help organizations monitor user actions and detect anomalies. If a user’s behavior deviates from established patterns, automated systems can trigger alerts or additional verification protocols. This proactive approach assists in identifying potential security threats before they escalate.
Benefits of Zero-Trust Security in Big Data Environments
The transition to a zero-trust security model offers numerous benefits for organizations working with Big Data:
1. Enhanced Data Security
The most significant advantage is the enhanced protection of sensitive data. By constantly verifying user identity and ensuring that access is strictly controlled, organizations can shield their data against internal and external threats.
2. Compliance with Data Regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies are imposing strict data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). A zero-trust approach facilitates compliance by adopting stringent access controls and data monitoring processes that align with these frameworks.
3. Increased Trust in Data Analytics
Implementing a zero-trust security model allows organizations to trust their analytics models more. When data access is meticulously controlled and monitored, the datasets used for analysis are less likely to be compromised, leading to more reliable insights and decision-making.
4. Agility in Operations
Big Data environments require agility to adapt to changing business landscapes. The zero-trust model enables organizations to securely expand their data analytics capabilities and utilize cloud resources without the persistent fear of security breaches.
Challenges of Implementing Zero-Trust in Big Data
While the benefits of a zero-trust security model are clear, implementing it in Big Data contexts can present challenges:
1. Overhaul of Legacy Systems
Many organizations rely on legacy systems that are not equipped to handle the demands of zero-trust security. Transitioning to modern platforms that support automated security features may require significant investment and time, making it a daunting task.
2. Cultural Change within Organizations
The shift to a zero-trust model often necessitates a cultural change within the organization. Employees accustomed to the traditional “trusted insider” philosophy may resist the changes involved in zero-trust, leading to potential friction and challenges in adoption.
3. Complexity in User Management
Managing user identities and permissions can become increasingly complex, particularly in organizations with a large number of employees or contractors. Ensuring compliance with the zero-trust model requires ongoing attention and resources to adjust permissions as roles evolve.
Future of Zero-Trust in Big Data
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the zero-trust security model will play an increasingly critical role in protecting Big Data environments. Organizations that adopt this model will find themselves better prepared to tackle the challenges of the digital landscape. Furthermore, the growing trend towards distributed systems and cloud computing makes the zero-trust framework a necessary component of a resilient security posture.
Ultimately, embracing the principles of zero-trust security can lead to not just improved data security but also a more robust data-driven culture capable of leveraging analytics effectively while safeguarding vital assets.
Implementing zero-trust security models is essential in safeguarding Big Data environments from potential threats and ensuring data integrity and privacy. By continuously verifying and authenticating users and devices accessing the data, organizations can strengthen their security posture and mitigate risks associated with Big Data operations. Embracing zero-trust principles is paramount in the ever-evolving landscape of Big Data to protect sensitive information and maintain trust with stakeholders.