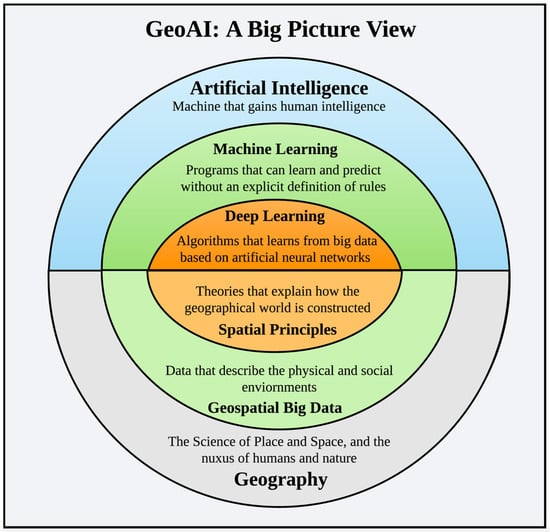
In the era of Big Data, the explosion of geospatial information has posed significant challenges in how to effectively process, analyze, and derive insights from massive amounts of location-based data. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a pivotal technology in handling large-scale geospatial Big Data, offering advanced capabilities such as machine learning, deep learning, and computer vision to uncover patterns and trends that were previously inaccessible. This article delves into the role of AI in harnessing the power of geospatial Big Data, exploring how AI-driven techniques are revolutionizing the processing and utilization of spatial data on a massive scale.
Understanding Geospatial Big Data
Geospatial Big Data refers to vast sets of data that are linked to locations and can include anything from satellite images to GPS data and social media check-ins. As the volume of geospatial data continues to grow, driven by advancements in technology and increased data collection capabilities, understanding how to effectively process and analyze this information becomes paramount. The challenge lies not only in the sheer scale of the data but also in the complexity of the data structures and the necessity for accurate interpretation.
The Intersection of AI and Geospatial Data
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a transformational role in processing large-scale geospatial big data. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI enhances the capability to extract meaningful insights from colossal amounts of geographical information. Here are several ways in which AI is reshaping the landscape of geospatial data analysis:
1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
AI algorithms facilitate the acquisition and preprocessing of geospatial data through techniques such as:
- Automated Data Collection: Drones and satellites, equipped with AI, capture high-resolution imagery, enabling large-scale data gathering.
- Data Cleaning: AI models identify and rectify inconsistencies and inaccuracies in the collected data, ensuring that only high-quality data is utilized for further analysis.
- Integration: Combining diverse data sources, including remote sensing data, social media feeds, and sensor data, can be streamlined by AI systems.
2. Advanced Data Analysis and Machine Learning
AI enhances data analysis capabilities through various machine learning techniques that allow for:
- Pattern Recognition: AI can detect patterns and trends in complex datasets that would be impossible for humans to discern, providing valuable insights.
- Predictive Analytics: By using historical data to predict future outcomes, AI helps in urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.
- Classification and Clustering: Algorithms categorize spatial data into meaningful groups, facilitating easier analysis and visualization.
3. Real-time Data Processing
The ability to process data in real-time is crucial for applications such as disaster response and traffic management. AI technologies contribute significantly by enabling:
- Streaming Analytics: Continuous analysis of incoming geospatial data allows for quick responses to changing conditions.
- Alert Systems: AI can trigger alerts based on predefined thresholds or anomalies, which is essential in emergency situations.
4. Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are vital tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing geospatial data. AI enhances GIS capabilities through:
- Intelligent Mapping: AI algorithms can create dynamic maps that adapt to real-time data changes, providing up-to-date information to decision-makers.
- Spatial Analysis: AI-powered GIS can perform complex spatial analyses, allowing users to derive insights such as optimal site selection or resource allocation.
5. Data Visualization and Interpretation
Visualizing geospatial data is essential for human understanding. AI improves data visualization through:
- Enhanced Graphics: AI tools create meaningful charts, graphs, and maps that tell compelling stories from raw data.
- Interactive Dashboards: Users can interact with data through AI-driven dashboards, facilitating easier exploration and manipulation of geospatial data.
6. Case Studies of AI in Geospatial Big Data
Numerous real-world applications exemplify the effectiveness of AI in processing geospatial big data:
- Urban Planning: Cities like New York use AI to analyze traffic patterns and manage public transport systems efficiently.
- Disaster Management: Organizations employ AI to predict natural disasters’ impacts by analyzing geological data and optimizing resource allocation.
- Agriculture: Farmers utilize AI to assess crop health and optimize irrigation practices through satellite data analysis.
7. Challenges in Integrating AI with Geospatial Big Data
While AI holds remarkable potential, integrating these technologies with geospatial big data presents several challenges:
- Data Privacy: Increased data collection heightens concerns over privacy and data security.
- Algorithm Bias: AI systems can unintentionally reflect biases present in training data, leading to skewed analysis.
- Scalability: Ensuring that AI solutions can scale to handle massive datasets effectively is a continual challenge.
8. Future Trends: AI and Geospatial Big Data
The future of AI in the geospatial big data domain promises exciting developments:
- Federated Learning: This method enables AI models to learn from decentralized data across multiple sources, enhancing privacy.
- Explainable AI: As AI systems become more complex, developing interpretable models will increase trust and adoption in geospatial applications.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to where it is generated will enable quicker analyses and reduce the burden on central data servers.
Conclusion: The Impact of AI on Geospatial Big Data Processing
As we witness ongoing advancements in AI technologies, their role in processing large-scale geospatial big data will only increase. Through improved data acquisition, analysis, and visualization techniques, AI stands to transform how we engage with and understand our world’s complex geographic data landscapes.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in processing large-scale geospatial Big Data offers immense potential for optimizing decision-making processes, deriving valuable insights, and driving innovation across various industries. By leveraging AI technologies such as machine learning and deep learning, organizations can effectively analyze and extract valuable information from vast geospatial datasets, leading to enhanced efficiencies, better resource allocation, and informed decision making. As the volume and complexity of geospatial Big Data continue to grow, the role of AI will be paramount in unlocking the full potential of these datasets and enabling organizations to gain a competitive edge in the era of Big Data.