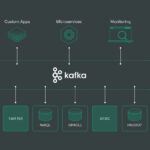
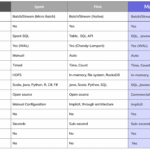
Google BigQuery plays a crucial role in the world of Big Data analytics by providing a powerful and scalable platform for processing and analyzing massive amounts of data in real-time. As organizations strive to leverage the insights hidden within their vast datasets, BigQuery offers high-speed querying capabilities, seamless integration with other Google Cloud services, and cost-effective storage options. With its distributed computing technology and SQL-like query language, Google BigQuery enables businesses to extract valuable information from their Big Data for making data-driven decisions and gaining a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world.
Understanding Google BigQuery
Google BigQuery is a fully managed, serverless data warehouse that enables scalable analysis over large datasets. Built on Google’s robust infrastructure, BigQuery allows users to focus on analyzing data rather than managing resources. This platform facilitates Big Data analytics by providing an SQL-like interface and powerful machine learning capabilities, making it a popular choice among organizations looking to leverage their data.
The Importance of Big Data Analytics
In today’s digital age, organizations collect vast amounts of data from various sources, including social media, IoT devices, and transaction logs. Effectively analyzing this data is crucial for gaining insights, enhancing decision-making, and driving business value. Big Data analytics transforms raw data into meaningful information, uncovering patterns and trends that would otherwise remain hidden.
Key Features of Google BigQuery
1. Scalability
One of the most compelling features of Google BigQuery is its scalability. As organizations encounter ever-growing datasets, BigQuery can seamlessly scale to handle petabyte-scale data. Users can execute complex queries without worrying about the underlying hardware, which is automatically managed by Google’s infrastructure.
2. Speed and Performance
BigQuery is designed for high-performance operations, providing fast query execution even on massive datasets. This speed is achieved through Google’s Dremel technology, which allows BigQuery to process queries in seconds rather than hours, facilitating real-time analytics.
3. Serverless Architecture
Being a serverless platform, Google BigQuery eliminates the need for users to manage server infrastructure. Organizations can allocate resources dynamically based on workload demands, reducing operational overhead and complexity.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
Google BigQuery employs a pay-per-query pricing model, which means organizations only pay for the data they process. This model enables businesses to manage costs effectively while utilizing powerful analytics capabilities without a substantial upfront investment.
5. Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
BigQuery integrates seamlessly with Google’s Machine Learning (ML) tools, allowing users to build and deploy ML models directly within the data warehouse. Features like BigQuery ML allow analysts to create machine learning models using standard SQL syntax, enhancing the accessibility of advanced analytics.
Use Cases for Google BigQuery in Big Data Analytics
1. Marketing Analysis
Organizations can leverage BigQuery for marketing analytics by analyzing customer behavior and campaign performance across multiple channels. By ingesting data from platforms like Google Analytics, social media, and CRM systems, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences and trends, enabling targeted marketing strategies.
2. Financial Analysis
Financial institutions utilize BigQuery to monitor transactions in real-time, detect fraudulent activities, and analyze customer spending patterns. BigQuery’s ability to handle large volumes of data in a short time frame makes it ideal for compliance with regulatory requirements and risk assessment.
3. Data Science and Research
Researchers and data scientists use BigQuery to analyze vast datasets for insights relevant to scientific studies and experiments. By combining BigQuery’s analytics capabilities with data visualization tools like Google Data Studio, researchers can create interactive dashboards and share findings easily.
4. IoT Data Processing
With the rise of IoT devices, organizations are inundated with sensor data. BigQuery enables the analysis of this data in real-time, making it possible to detect anomalies, monitor performance, and optimize usage patterns in various applications ranging from manufacturing to smart cities.
Data Security and Compliance in BigQuery
As data privacy regulations tighten globally, it’s critical for businesses to ensure compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA. Google BigQuery provides robust security features, including data encryption at rest and in transit, Identity and Access Management (IAM), and audit logs. These features help organizations manage access securely while maintaining compliance with data regulations.
Integrating Google BigQuery with Other Google Cloud Services
BigQuery integrates with a range of Google Cloud services, creating a cohesive Big Data ecosystem. For instance:
- Google Cloud Storage (GCS): Data can be easily loaded into BigQuery from GCS, allowing for efficient storage and retrieval.
- Google Cloud Dataflow: This service can be used to preprocess and transform data before ingestion into BigQuery, enabling more complex ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) workflows.
- Google Data Studio: Users can visualize BigQuery data through Google Data Studio, creating reports and dashboards that help stakeholders make informed decisions.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Learning Curve
Although BigQuery uses a familiar SQL-like syntax, organizations may face a learning curve if their teams are accustomed to traditional data warehouses. Continuous training and resources are necessary to harness the full potential of BigQuery.
2. Data Governance
Implementing proper data governance policies is vital when using BigQuery. Organizations need to establish clear guidelines on who can access what data, how data is managed, and how data quality is maintained.
3. Network Dependence
Being a cloud-based service, BigQuery relies on consistent internet connectivity. Organizations should ensure that they have robust networking solutions in place to avoid disruptions in their analytics operations.
Conclusion
With its powerful features, scalability, and integration capabilities, Google BigQuery plays a pivotal role in Big Data analytics. It empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions and enhances their ability to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of data efficiently. As the landscape of Big Data continues to evolve, BigQuery remains at the forefront, offering the tools and capabilities needed for successful analytics.
Google BigQuery plays a crucial role in Big Data analytics by offering a powerful, scalable, and cost-effective platform for processing and analyzing large volumes of data. Its ability to handle massive datasets quickly and efficiently makes it a valuable tool for organizations seeking to derive actionable insights from their data. Overall, Google BigQuery significantly contributes to the success of big data analytics initiatives by enabling data-driven decision-making and driving innovation in various industries.