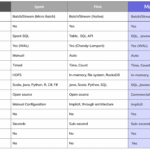
In the realm of Big Data, the importance of robust and relevant data for training machine learning models cannot be overstated. Synthetic data, generated through computer algorithms rather than collected from real-world sources, plays a crucial role in this process. By providing scalable and diverse datasets that mimic the characteristics of real data, synthetic data enables organizations to train their Big Data models more effectively and efficiently. This article explores the significance of synthetic data in the context of training Big Data models and highlights its potential to revolutionize the way organizations leverage data for advanced analytics and decision-making.
Synthetic data is emerging as a pivotal component in the realm of Big Data, especially when it comes to training models that require massive datasets for effective learning. Traditional data collection methods can be resource-intensive, time-consuming, and sometimes even impractical. As organizations strive for deeper insights and better predictive analytics, the integration of synthetic data into their data science workflows becomes increasingly relevant.
What is Synthetic Data?
Synthetic data refers to artificially generated information that mimics the statistical properties and structures of real-world data. Unlike traditional datasets, which are collected from actual events, synthetic datasets are produced using algorithms and models. These can include mathematical models, simulation techniques, or generative models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
Why Synthetic Data is Important for Big Data Models
Big data models often operate under constraints related to data availability, quality, and privacy. Here are several reasons why synthetic data is crucial in this landscape:
1. Overcoming Data Scarcity
In many industries, obtaining enough data to train robust machine learning models is a challenge. For instance, in healthcare, patient data is limited due to privacy regulations. Synthetic data provides a viable solution by generating large amounts of data without compromising real patient information.
2. Enhancing Data Diversity
Many datasets suffer from bias due to a lack of diversity among samples. By utilizing synthetic data, organizations can generate a variety of scenarios, thereby improving model training. This is particularly valuable in fields like autonomous driving, where vehicles must be trained across numerous edge cases that are rarely captured in real-world datasets.
3. Maintenance of Data Privacy
With data privacy laws such as GDPR and CCPA, organizations must be cautious about using real user data, particularly in sensitive areas like finance and healthcare. Synthetic data can be used to train models without exposing any real individual’s data, thus remaining compliant with regulations.
4. Cost-Effective Solutions
Collecting and labeling data can incur significant costs, especially for large-scale datasets. By utilizing synthetic data, businesses can save on these expenses, reducing the financial burden associated with data acquisition and preparation.
Applications of Synthetic Data in Big Data
The use of synthetic data spans a variety of sectors, enhancing the training of big data models in numerous applications.
1. Finance and Risk Assessment
In the financial sector, synthetic datasets can simulate various market conditions and consumer behaviors. This allows firms to train their risk assessment models effectively, helping in fraud detection and credit scoring while ensuring that real personal data isn’t misused or exposed.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, synthetic data can be generated to reflect patient demographics, conditions, and treatment responses. This data can be essential for designing effective clinical trials, developing treatment protocols, and training predictive health models without compromising patient confidentiality.
3. E-commerce and Recommendation Systems
Synthetic data can also enhance the training of recommendation systems in e-commerce. By generating customer behavior data, companies can refine algorithms to provide personalized product suggestions, improving user experience and boosting sales.
4. Autonomous Systems
In the realm of autonomous vehicles and drones, synthetic data is invaluable for simulating various driving conditions, obstacles, and unforeseen situations. This data helps improve the robustness of machine learning models, ensuring safety and reliability in real-world operations.
Best Practices for Using Synthetic Data in Model Training
While synthetic data presents numerous advantages, there are best practices to follow to maximize its effectiveness:
1. Combine Real and Synthetic Data
Using a hybrid approach that combines both real and synthetic data can lead to better model performance. Real data provides the authenticity that synthetic data mimics, improving the model’s ability to understand true-world complexities.
2. Validate Synthetic Data
Before integrating synthetic data into model training, it’s essential to validate its quality. Ensuring that the synthetic data accurately reflects the distributions and relationships found in real data is critical for effective model training.
3. Monitor Performance
When training models using synthetic data, continuous monitoring of their performance will help identify areas for improvement. By analyzing results, data scientists can refine synthetic data generation methods and improve model accuracy.
4. Leverage Advanced Generative Models
Utilizing sophisticated generative models, such as GANs, can lead to producing more realistic and higher quality synthetic datasets. These models can adapt to various complexities and are capable of generating detailed, nuanced datasets that mimic real-world scenarios.
Challenges Associated with Synthetic Data
While the use of synthetic data offers numerous benefits, there are inherent challenges to consider:
1. Quality Control
Creating high-quality synthetic data is not trivial. Poorly generated synthetic data can lead to misleading outcomes and flawed model predictions. Quality control measures should be a priority to ensure that synthetic datasets meet necessary standards.
2. Complexity of Modeling
The complexity involved in creating models that can generate effective synthetic data can require significant expertise. Organizations may need to invest in specialized skills, tools, and technologies to develop these models successfully.
3. Risk of Overfitting
When models are trained predominantly on synthetic data, there is a risk of overfitting to the patterns present in it, which may not generalize well to real-world applications. It’s crucial to strike a balance in the data used for training.
The Future of Synthetic Data in Big Data Training
The future of synthetic data is promising, with the potential to redefine how big data models are trained. Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning will likely lead to more sophisticated methods for generating synthetic data that can more accurately reflect real-world conditions.
As organizations continue to embrace these technologies, making the best use of synthetic data will be key. From improving operational efficiency to safeguarding consumer privacy, synthetic data holds a vital role in cultivating smarter, more accurate Big Data models that can empower businesses to make data-driven decisions.
Synthetic data plays a crucial role in training big data models by addressing data scarcity and privacy concerns, enabling more robust and efficient model development. Its ability to replicate real-world scenarios and generate diverse data sets contributes significantly to enhancing the performance and accuracy of big data models. As big data continues to drive innovation and decision-making across various industries, the use of synthetic data provides a valuable solution to overcome challenges associated with data availability and quality, thus unlocking the full potential of big data analytics.