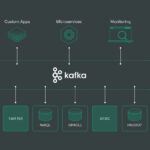
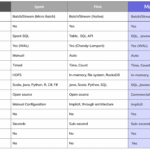
Big Data has become a ubiquitous term in today’s digital age, but what exactly does it mean? Simply put, Big Data refers to the massive volume of structured and unstructured data that is generated by businesses and individuals every day. This data encompasses a wide range of sources, including social media, sensors, mobile devices, and online transactions. The key characteristics of Big Data are its volume, velocity, and variety – making it challenging to manage and analyze using traditional data processing tools. In this beginner’s guide, we will explore the importance of Big Data, its impact on various industries, and the tools and techniques used to extract valuable insights from this wealth of information. Let’s dive into the world of Big Data and uncover its immense potential for driving innovation and informed decision-making.
Big Data refers to large volumes of data that can be analyzed computationally to reveal patterns, trends, and associations, especially concerning human behavior and interactions. The concept encompasses not just the sheer volume of data but also the velocity at which it is generated and the variety of formats in which it exists.
Understanding the 3 Vs of Big Data
To grasp the essence of big data, it is essential to understand its three core characteristics, often referred to as the 3 Vs: Volume, Velocity, and Variety.
Volume
Volume refers to the sheer amount of data being generated every second. With the rise of social media, IoT devices, and digital transactions, we are producing zettabytes of data daily. Organizations are now challenged to not only store this data but extract meaningful insights from it.
Velocity
Velocity denotes the speed at which data is generated and processed. Real-time data feeds from social media, transactional records, and sensors mean that businesses can gain insights nearly instantaneously. This rapid flow of data requires robust processing capabilities to ensure timely decision-making.
Variety
Variety highlights the different formats and types of data being generated. This can include structured data (like databases and spreadsheets), semi-structured data (like XML and JSON), and unstructured data (like videos, text files, and social media posts). Understanding how to handle these diverse data types is crucial for effective data analysis.
Types of Big Data
Big data can be categorized into four main types, based on its source and usage. These types include:
Structured Data
Structured data is organized data that resides in fixed fields within a record or file. This data is easily searchable using straightforward algorithms. Examples include databases, spreadsheets, and tables that store customer information or sales transactions.
Semi-Structured Data
Semi-structured data does not reside in a relational database but still has some level of organization. Examples include emails, XML files, and JSON files, which contain tags that make it easier to analyze the information even though it doesn’t follow a strict format.
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data is information that does not have a predefined data model. This type of data includes images, audio files, video files, and text documents, making analysis and extraction more complex.
Metadata
Metadata provides information about other data. It helps in data management by organizing and categorizing different types of data for better accessibility and understanding. For example, the metadata of a photo might include the time it was taken, the camera settings, and the location.
Importance of Big Data
The significance of big data can be seen across various sectors. Here are some of the primary reasons why it is critical for modern businesses:
Enhanced Decision-Making
By analyzing big data, companies can make informed decisions backed by analytics rather than hunches. Real-time data analysis leads to more accurate predictions and strategies that can enhance overall business performance.
Customer Insights
Big data enables organizations to understand customer preferences and behaviors better. This information can help tailor marketing strategies, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. For instance, e-commerce platforms can recommend products based on user behavior analysis.
Operational Efficiency
Businesses can streamline operations by leveraging big data analytics. By analyzing process data, organizations can identify inefficiencies, optimize supply chains, and reduce operational costs.
Competitive Advantage
Companies that effectively utilize big data can gain a significant advantage over competitors. These businesses can spot market trends, customer needs, and risks faster and more accurately, enabling them to stay ahead.
Big Data Technologies
Several technologies contribute to the management and analysis of big data. Below are some of the most commonly used:
Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers. Hadoop is designed to scale from a single server to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage.
NoSQL Databases
NoSQL databases are designed to handle unstructured and semi-structured data. Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL systems like MongoDB and Cassandra provide flexibility in terms of the structure of data and can cope with high-velocity data streams.
Data Lakes
A data lake is a centralized repository that allows you to store all your structured and unstructured data at any scale. You can run different types of analytics to help with visualization, predictive analysis, and machine learning.
Machine Learning and AI
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) are integral components in processing big data. These technologies enable computers to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
Challenges of Big Data
While the potential of big data is significant, it comes with its challenges, including:
Data Privacy
With the vast amount of personal data being collected, ensuring data privacy has become a crucial concern. Organizations must comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to protect user information.
Data Quality
Data quality is paramount when analyzing big data. Poor-quality data can lead to inaccurate insights and flawed decision-making. Organizations must implement robust data cleansing and validation processes.
Cost of Storage and Processing
As data volumes grow, the costs associated with storing and processing big data can escalate. Companies need to strike a balance between processing capabilities and budget constraints.
Skills Gap
There is a growing demand for skilled professionals in big data analytics, but the shortage of qualified talent poses a significant challenge for organizations looking to leverage big data effectively.
Future of Big Data
The future of big data looks promising as more organizations become aware of its benefits. Key trends to watch include:
Integration of AI and ML
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with big data analytics will enhance the accuracy and efficiency of data processing and insights generation.
Edge Computing
Edge computing allows data to be processed closer to its source, reducing latency and bandwidth use. This is particularly useful for IoT devices, which generate vast amounts of data that need to be analyzed in real-time.
Increased Focus on Data Security
As data breaches become increasingly common, organizations will invest more in data security measures. Technologies like blockchain may emerge as solutions to ensure the integrity and security of big data.
The big data landscape continues to evolve, with exciting opportunities for businesses ready to embrace data-driven decision-making. Understanding its complexities and harnessing its potential can indeed transform the operational strategies of many organizations across various industries.
Big Data encompasses the massive volume, variety, and velocity of data generated and collected in today’s digital world. Understanding and effectively utilizing Big Data can provide valuable insights, drive innovation, and create competitive advantages for businesses across various industries. Embracing the potential of Big Data can lead to enhanced decision-making, improved customer experiences, and overall organizational success in the era of data-driven growth.