Implementing API access management with OAuth scopes is crucial when designing secure and controlled access to APIs in a web service environment. OAuth scopes allow for granular control over what actions and data resources an application can access through an API. By defining and assigning scopes to different API endpoints, developers can enforce fine-grained authorization policies, ensuring that only authorized clients can access specific functionalities within the API. This enhances security by minimizing potential risks associated with unauthorized access and misuse of sensitive data. In this article, we will explore the importance of OAuth scopes in API access management and discuss best practices for their implementation in the context of APIs and web services.
Understanding API Access Management
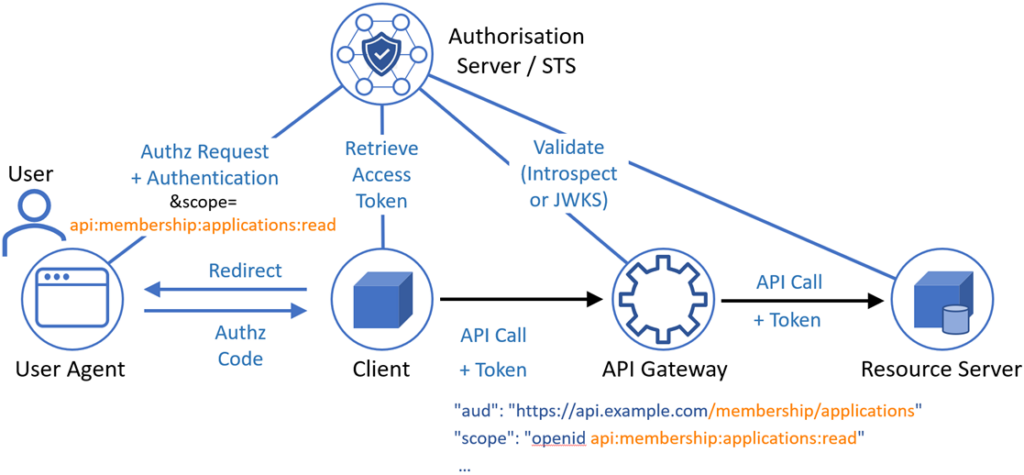
API access management is crucial for ensuring that your APIs are secure and that users can only access the resources they are authorized to. Implementing access management protocols, such as OAuth, helps in controlling who gets access to what. By defining and enforcing OAuth scopes, you can enhance your API’s security while providing flexibility in how your services are consumed.
What are OAuth Scopes?
OAuth scopes are used in the OAuth protocol to limit the access an application has to a user’s data. They provide a way to specify the types of access your application requests, ensuring that users only provide the minimal permissions necessary for your app to function. For example, a social media application might request different scopes for reading a user’s profile and posting on their behalf.
Benefits of Using OAuth Scopes
- Granular Access Control: OAuth scopes allow you to specify exactly what API endpoints an access token can interact with.
- Enhanced Security: By restricting access based on scopes, sensitive data remains protected, reducing the risk of exposure.
- User Transparency: Users can see what permissions they are granting and can make informed decisions about the data they share.
- Flexibility: Different scopes enable developers to create tailored experiences while adhering to the principle of least privilege.
Setting Up OAuth for API Access Management
Implementing OAuth requires a systematic approach. Below are the steps you need to follow:
Step 1: Choosing an OAuth 2.0 Framework
No matter what programming language or framework you are using, there is most likely an OAuth 2.0 library available. Select a framework that best suits your architecture; some popular choices include:
- Spring Security OAuth for Java
- ASP.NET Core Identity for .NET
- Auth0 for Node.js and serverless applications
- OAuthLib for Python
Step 2: Register Your Application
To use OAuth, you must register your application with the Authorization Server. This registration typically provides:
- Client ID: A unique identifier for your application.
- Client Secret: A secret known only to your application and the authorization server.
- Redirect URIs: URIs where the authorization server can send authentication responses.
Step 3: Define OAuth Scopes
Now it’s time to define the various OAuth scopes you’ll need. Consider the following guidelines:
- Identify the resources your API will expose and determine the level of access required for each resource.
- Utilize descriptive names for scopes to improve user comprehension. For instance, use
read_profileinstead ofscope1. - Group related permissions together to simplify user decisions. For example, a
profilescope could encompass multiple related permissions.
Step 4: Implementing OAuth Grants
OAuth 2.0 defines several grants, but the most common are the Authorization Code, Implicit, Resource Owner Password Credentials, and Client Credentials grants. Choose the right grant type depending on your application:
- Authorization Code Grant: Best for server-side applications that require secure token exchanges.
- Implicit Grant: Suitable for browser-based applications, though less secure.
- Resource Owner Password Credentials Grant: Used in trusted applications where users provide username and password directly.
- Client Credentials Grant: Ideal for machine-to-machine communication.
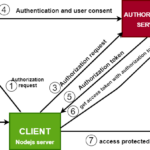
Step 5: Requesting Access Tokens
Once your application registers the necessary OAuth scopes, it can request an access token using a specific grant flow. The process often looks like this:
- The application redirects the user to the authorization server to prompt for login.
- The user logs in and authorizes the requested scopes.
- The authorization server redirects the user back to the application’s specified URI with an authorization code.
- The application exchanges this code for an access token, specifying the scopes it is requesting.
Step 6: Using Access Tokens with Scopes
Once you have received an access token, use it to authenticate API requests. The access token will contain information about the scopes granted:
- Verify the validity of the token with your API’s resource server.
- Check the scopes associated with the token to determine if the user has permission to access the requested resource.
Best Practices for Managing OAuth Scopes
Secure Your Client Secrets
Store your client secrets securely. Avoid hardcoding them in your application code or leaking them via version control systems.
Regularly Review Your Scopes
Continuously analyze the scopes your application is requesting. Eliminate any that are no longer necessary to minimize risk.
Monitor and Log Access
Establish logging for OAuth token requests and access events. This practice helps in auditing and tracking any unauthorized access attempts.
User Education
Educate your users about the scopes your application requires. Clear communication helps build trust and increases the likelihood of user acceptance.
Implement Token Expiry and Revocation
Implement access token lifetimes and allow users to revoke tokens when necessary. This approach ensures that even if a token is compromised, it cannot be used indefinitely.
Conclusion
Implementing API access management with OAuth scopes is a vital task for securing your APIs and web services. By following the guidelines and steps outlined above, you can effectively manage user access to your API while enhancing security and user trust. Start implementing these practices today to safeguard your development environment.
Implementing API access management with OAuth scopes is essential for controlling access to resources within an API. By defining specific scopes for different types of actions or data, organizations can ensure that only authorized parties have the necessary permissions to interact with their APIs securely. This helps maintain data privacy, security, and overall API integrity.