Building a secure API with Zero Trust Architecture is crucial in today’s interconnected digital world where APIs and web services play a pivotal role in enabling seamless interactions between various systems and applications. Zero Trust Architecture shifts the traditional security paradigm from a perimeter-based approach to a mindset where trust is never assumed, not even within the internal network. This approach emphasizes the need to authenticate, authorize, and encrypt every interaction, whether it is within the network or across different systems. In this introduction, we will explore key considerations and best practices for building a secure API with Zero Trust Architecture to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of your systems and services.
Understanding Zero Trust Architecture
In the realm of API security, the concept of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has emerged as a robust approach to safeguarding sensitive data. Unlike traditional security models that rely on perimeter defenses, Zero Trust operates on the principle of trusting no one by default, whether they are inside or outside the network. This radical shift necessitates implementing stringent verification methods and continuous monitoring of all entities interacting with your API.
The Pillars of Zero Trust Architecture
Building a secure API under the framework of Zero Trust involves several critical pillars:
- Identity Verification: Every user, device, and application must authenticate before gaining access.
- Least Privilege Access: Users should have only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their tasks.
- Network Segmentation: Properly segmenting the network to limit lateral movement enhances security.
- Continuous Monitoring: Continuous visibility into the environment helps in identifying anomalies.
- Data Protection: Ensuring encryption of data in transit and at rest is essential.
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) is foundational to implementing a Zero Trust API. IAM encompasses various strategies such as:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforced MFA for all users adds an extra layer of security beyond just usernames and passwords.
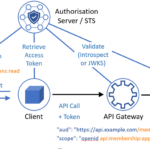
- OAuth and OpenID Connect: These protocols allow secure delegated access, facilitating user identity verification and authorization.
- API Gateway: Functioning as a central point for managing API access, an API gateway can enforce IAM policies effectively.
2. Implementing Least Privilege Access
In a Zero Trust model, applying the least privilege principle limits user access based on their role. Key strategies include:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define user roles and allocate permissions strictly based on those roles.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): A more dynamic approach where access is granted based on attributes such as time of access, location, etc.
- Policy Enforcement: Regularly review and update access policies to adapt to changing business requirements.
3. Network Segmentation and Microsegments
Network segmentation divides the system into smaller, manageable segments or segments them into microsegments. This strategy is crucial in a Zero Trust framework for:
- Minimizing Attack Surfaces: By limiting access to sensitive API data, networks reduce potential attack vectors.
- Controlling Lateral Movement: In the event of a breach, segmentation slows down the intruder’s ability to access additional resources.
- Improving Monitoring and Forensics: Isolated segments simplify monitoring and response to security incidents.
4. Encryption Protocols
Employing strong encryption protocols is non-negotiable in a robust API security posture. Key considerations include:
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): Use TLS to encrypt data in transit, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential.
- Data Encryption: Implement strong encryption algorithms for data at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Key Management: Maintain strict protocols for key generation, distribution, and revocation to enhance security.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Zero Trust emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring for timely detection of threats. This includes:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Employ IDS to analyze traffic and identify suspicious activities.
- Anomaly Detection: Implement machine learning algorithms to spot unusual access patterns that could indicate breaches.
- Comprehensive Logging: Maintain logs of all API transactions for forensic analysis and regulatory compliance.
6. API Gateway Security Features
An API gateway plays a vital role in enforcing Zero Trust principles. Key features include:
- Throttling and Rate Limiting: Protect your APIs against abuse by limiting the number of requests from clients.
- Input Validation: Prevent injection attacks by rigorously validating input parameters.
- Security Policies: Define and enforce granular security policies at the API gateway level.
7. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Proactively identifying weaknesses in your API and its infrastructure is crucial. Regular security audits and penetration testing help in:
- Vulnerability Assessment: Conduct periodic assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in your API and supporting services.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure that your API adheres to regulatory requirements relevant to your industry.
- Incident Response Testing: Test your incident response plan regularly to ensure swift mitigation in case of an actual breach.
8. Fostering a Security-First Culture
Finally, creating an organizational culture that prioritizes security is essential for the success of a Zero Trust Architecture. Strategies include:
- Security Training: Conduct regular training sessions for all employees to instill security awareness.
- Encouraging Reporting: Foster an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious activities.
- Collaboration Between Teams: Promote collaboration among development, security, and operations teams to embed security into the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
9. Leveraging Advanced Technologies
Integrating advanced technologies can enhance your API security strategy. Consider implementing:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Leverage AI for automated monitoring and threat detection.
- Blockchain: Utilize blockchain technology to secure transactions and user identities across distributed applications.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Deploy ZTNA solutions to reinforce secure access regardless of the user’s location.
10. Conclusion
Building a secure API with Zero Trust Architecture is an ongoing process that requires adherence to best practices and continuous improvement. By implementing the strategies and principles outlined above, organizations can significantly enhance their API security posture and safeguard sensitive data against evolving cyber threats.
Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture is crucial in building a secure API environment. By continuously verifying and validating all users and devices accessing the API, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Incorporating strong authentication methods, encryption, and detailed monitoring will strengthen the overall security posture of the API, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected at all times.