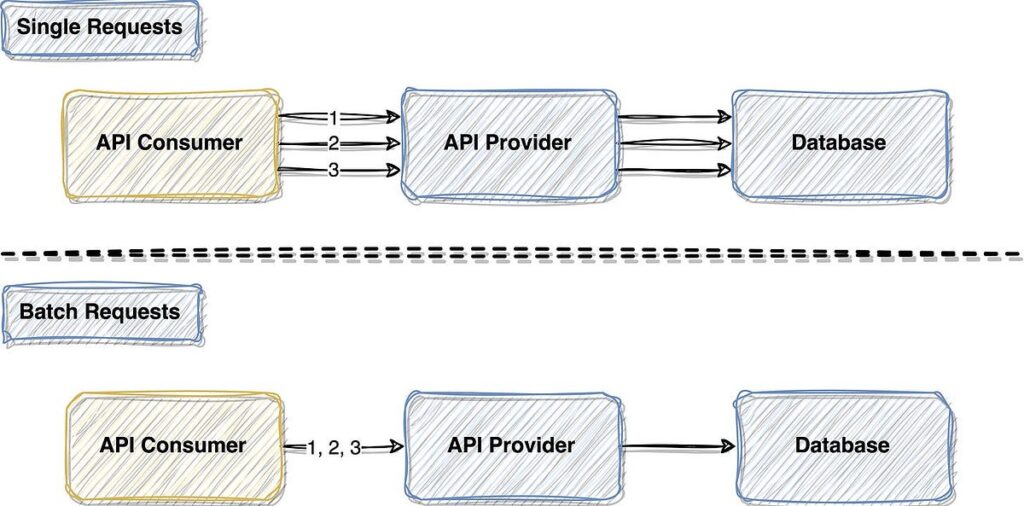
When working with APIs and web services, one common technique for improving performance is by implementing API request batching. Request batching involves combining multiple API requests into a single request, thereby reducing the overhead associated with making multiple individual requests. By batching requests, you can minimize network latency, decrease the number of connections established with the server, and optimize overall resource utilization. This ultimately leads to improved efficiency and better performance for your application. In this guide, we will explore the benefits of API request batching and provide insights on how to effectively implement this technique to optimize the performance of your APIs and web services.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, optimizing the performance of your APIs and web services is crucial for providing a seamless user experience. One effective technique to enhance performance is through API request batching. This article will delve deep into the concept of API request batching, its benefits, best practices, and how to implement it effectively.
What is API Request Batching?
API request batching is a technique that allows developers to send multiple API requests in a single network call. Instead of making separate requests for each operation, which can lead to increased latency and congestion, batching consolidates these requests into a single payload.
This method not only reduces the number of HTTP requests made to the server but also improves the server’s ability to process data, resulting in faster response times and overall improved performance.
Benefits of API Request Batching
1. Reduced Latency
By minimizing the number of network calls, request batching can significantly lower latency. Each HTTP request incurs overhead due to connection setup, SSL negotiation, and data transfer, which can add up quickly. Batching allows you to negate much of this overhead, yielding quicker responses.
2. Improved Throughput
When multiple requests are sent in a batch, the server can handle them more efficiently. Since it knows that multiple requests are coming from the same client in a single call, it can optimize processing, which can lead to enhanced throughput.
3. Lower Bandwidth Usage
Less HTTP overhead means lower bandwidth utilization. Sending fewer requests can reduce the data transferred over the network, facilitating a smoother experience for users and saving costs on data transfer for developers.
4. Enhanced User Experience
End users benefit from a faster application, as data loads more efficiently with fewer requests. This leads to an overall more responsive user interface and contributes to user satisfaction.
Understanding Different Batching Strategies
Implementing API request batching can take various forms, and it’s essential to understand the different batching strategies available to choose the best approach for your application.
1. Array of Requests
The simplest and most common method is sending an array of requests in one API call. The server processes each request individually and returns an aggregated response. For example:
{
"requests": [
{"method": "GET", "path": "/users/1"},
{"method": "GET", "path": "/users/2"},
{"method": "POST", "path": "/users", "body": {"name": "New User"}}
]
}2. Composite Resources
In this strategy, you create composite resources within your API. For instance, instead of querying individual resources, you might have an endpoint that retrieves multiple entities together. This reduces the need for multiple calls:
GET /users?ids=1,2,33. Operations Command Pattern
Another approach is the operations command pattern where you define specific operations or scripts that dictate the actions the API should perform in a single request. This method can simplify transaction processing for bulk operations.
Key Considerations for Implementing API Request Batching
While API request batching offers substantial benefits, several considerations must be addressed during implementation to ensure success:
1. Payload Size
Many APIs impose limits on the maximum payload size. Be mindful of this limitation when designing your batching strategy. Sending too large a batch may result in partial processing or rejection of the requests.
2. Error Handling
When processing multiple requests, error handling becomes more complex. Decide how to handle errors for individual requests within a batch. Implement a robust mechanism to convey back the status of each request clearly.
3. Rate Limiting
API providers often enforce rate limits to prevent abuse. When implementing request batching, ensure that you adhere to these limits. Sending a large batch could push you over the threshold, leading to rejected requests.
4. Consistency and Idempotency
When creating batch requests, be aware of how operations may affect the state of your application. Ensure that modifications are idempotent where necessary, meaning that repeating the operation won’t have unintended side effects.
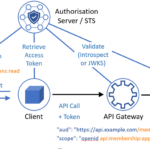
5. Security Concerns
Batching requests might increase security challenges. Ensure that proper authentication and authorization are applied to all requests in a batch, protecting your application from potential threats.
Best Practices for API Request Batching
1. Keep Batches Reasonably Sized
Divide large batching requests into smaller batches to maintain a balance between performance and reliability. Ideally, the batch size should be determined based on common payload sizes, API performance, and feedback from testing.
2. Monitor and Log Requests
Implement logging and monitoring to track batch requests’ performance metrics, identify bottlenecks, and analyze user interactions. This data can be pivotal for future optimization.
3. Test Extensively
Before deploying batching requests in a production environment, conduct extensive testing across various scenarios. This includes checking error handling, load testing, and analyzing how to handle different payload sizes.
4. Document Your API
Provide detailed documentation about the batching capabilities of your API. This includes sample requests/responses, error codes, and guidelines for optimal usage. Clear documentation helps developers understand how to best utilize batching.
5. Adapt to usage patterns
Make the batching implementation adaptive to user behavior by analyzing how users interact with the application. This can help fine-tune the batch size and composition dynamically based on real usage patterns.
Examples of API Request Batching Implementations
1. GraphQL
GraphQL inherently supports batching through its query structure, where clients can request multiple fields and nested resources in a single query. By leveraging GraphQL’s capabilities, developers can achieve significant performance gains.
2. REST APIs with Batching Endpoints
Many REST APIs have “batch” specific endpoints. For instance, a social media API might implement a batch endpoint, allowing you to fetch user profiles in a single request:
POST /api/v1/users/batch
{
"ids": [1, 2, 3]
}3. Firebase Firestore
Firestore allows batch operations for multiple write requests. This means you can execute multiple `set`, `update`, or `delete` operations in a single request, which can improve the performance of your data manipulation tasks.
Conclusion
By implementing API request batching, you can enhance the performance and efficiency of your APIs and web services. Applying best practices and understanding the nuances of batching can lead to significant improvements in both user experience and resource usage. Start incorporating batching techniques into your API strategy today for optimized performance.
Implementing API request batching is a powerful technique for optimizing performance in APIs and web services. By consolidating multiple individual requests into a single batch request, unnecessary overhead can be reduced, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced latency. This approach can significantly enhance the scalability and responsiveness of applications, leading to a better overall user experience. It is essential to consider factors such as payload size, data dependencies, and error handling when implementing API request batching to ensure its successful integration into your system.