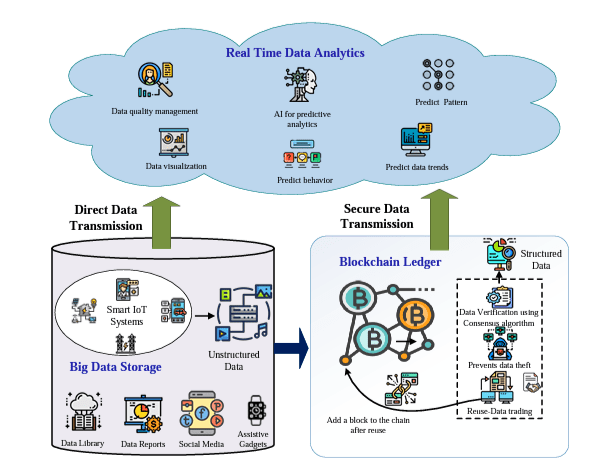
In the realm of Big Data, maintaining the security and integrity of vast amounts of information is paramount. Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool for secure data storage, offering decentralized and tamper-proof mechanisms to safeguard valuable data assets. This innovative approach to data storage not only enhances security measures but also ensures traceability and transparency in the handling of Big Data. In this article, we will delve into the role of blockchain in secure Big Data storage, exploring its benefits and implications for organizations dealing with massive datasets in today’s data-driven world.
In an era where Big Data is transforming industries and shaping decision-making processes, the challenge of securely storing this expansive amount of information has become more crucial than ever. Traditional data storage methods often fall short of the security and reliability required for sensitive and vast datasets. This is where blockchain technology plays a pivotal role, providing a revolutionary approach to data storage that enhances security, transparency, and integrity.
Understanding Big Data
Before diving into the intersection of blockchain and Big Data, it is essential to understand what Big Data entails. Big Data refers to datasets that are so large and complex that they become difficult to process using traditional data processing applications. It involves structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data from various sources, including social media, IoT devices, business transactions, and more.
Key characteristics of Big Data include:
- Volume: Refers to the sheer amount of data generated every minute.
- Velocity: The speed at which new data is generated and processed.
- Variety: The different formats and types of data, which can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
- Veracity: The quality of the data and its credibility.
- Value: The potential insights and benefits derived from analyzing the data.
The Need for Secure Data Storage
As organizations accumulate vast amounts of data, they face significant challenges regarding data privacy, security, and compliance with various regulations like the GDPR and CCPA. Data breaches are becoming increasingly common, threatening both organizations and their customers. Therefore, businesses must implement secure data storage solutions that not only protect sensitive information but also ensure data integrity and compliance with legal standards.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows data to be stored across a network of computers in a manner that is secure and tamper-proof. Each block in the blockchain contains a collection of records or transactions and is linked to the previous block, creating an immutable chain. Key features of blockchain technology include:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional databases, blockchain does not rely on a central authority to manage data.
- Transparency: Changes made to the blockchain are visible to all participants in the network, promoting accountability.
- Security: Cryptographic algorithms ensure that only authorized parties can alter the data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it is virtually impossible to modify or delete without consensus from the network.
The Convergence of Blockchain and Big Data
The integration of blockchain technology into Big Data storage solutions opens up new avenues for secure data management. Here are several key ways in which blockchain enhances Big Data storage:
1. Enhanced Security
Security is a top concern for organizations handling sensitive data. By leveraging blockchain, organizations can enhance data security through various means:
- Data Encryption: Each transaction or record stored on the blockchain is encrypted, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized individuals to access the information.
- Access Control: Smart contracts can be utilized to establish permission settings, allowing only authorized users to access or modify data.
- Audit Trails: With every change recorded on the blockchain, companies can maintain an immutable audit trail, enabling easier tracking of alterations and access.
2. Improved Data Integrity
The issue of data integrity is paramount in Big Data. Blockchain’s architecture ensures that data cannot be tampered with once it has been recorded. This immutability guarantees that:
- Data Remains Unchanged: Changes require consensus amongst the network participants, making unauthorized alterations nearly impossible.
- Trust in Data Sources: Organizations can verify the authenticity of their data sources through blockchain validation mechanisms.
3. Streamlined Data Sharing
Collaboration between different entities is essential in the Big Data landscape. Blockchain can facilitate secure data sharing among organizations, enabling:
- Controlled Access: Companies can share data seamlessly while retaining control over who can access specific datasets.
- Real-Time Updates: The decentralized nature of blockchain allows instantaneous updates, ensuring all parties have access to the latest information.
4. Cost Reduction
Storing and managing large datasets can be expensive. Blockchain technology reduces costs associated with:
- Data Management: The decentralized model eliminates the need for costly intermediary services.
- Data Security Measures: By incorporating built-in security measures, organizations can decrease their reliance on external security systems.
5. Compliance and Data Privacy
With stricter regulations surrounding data protection, blockchain technology can assist organizations in achieving compliance through:
- Decentralized Control: Data ownership can be transparent and decentralized, aligning with data sovereignty regulations.
- Automated Compliance: Smart contracts can execute predefined terms automatically, ensuring compliance without manual intervention.
Challenges in Combining Blockchain with Big Data
While the integration of blockchain in Big Data storage presents significant advantages, it is not without challenges. Some of these challenges include:
- Scalability: Blockchain networks can face challenges in scalability as the amount of data and transactions increases.
- Energy Consumption: Some blockchain protocols, particularly those using Proof of Work, consume significant amounts of energy, raising sustainability concerns.
- Complexity and Knowledge Gap: The current technology landscape may present potential skills gaps and complexities that could hinder widespread adoption.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Big Data Storage
The utilization of blockchain for Big Data storage is already evident across various sectors:
1. Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, blockchain can securely store patient records, ensuring that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized personnel, while also enabling seamless sharing among healthcare providers for better patient outcomes.
2. Finance
Financial institutions leverage blockchain to store transaction data securely, preventing fraud and ensuring accurate record-keeping through immutable ledgers. This enhances the integrity of financial data and reduces discrepancies.
3. Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, blockchain helps authenticate the origin of products, allowing companies to trace the product journey while enhancing data transparency between all parties involved, from manufacturers to consumers.
4. Government
Governments can use blockchain for securely storing citizen data, ensuring transparency in public records, and improving services through efficient data sharing while preserving privacy.
Conclusion
The intersection of blockchain technology and Big Data presents a transformative opportunity to enhance the security and integrity of data storage solutions. As organizations continue to navigate the challenges posed by vast datasets and stringent security requirements, the combination of these two powerful technologies offers a promising pathway toward more secure and reliable data management systems.
Blockchain technology offers a promising solution for secure Big Data storage by providing decentralized, tamper-proof, and transparent mechanisms for data management. By combining the strengths of blockchain with Big Data systems, organizations can enhance data security, integrity, and trustworthiness in an increasingly data-driven world.