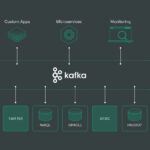
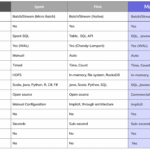
In today’s digital landscape, organizations are increasingly leveraging Big Data to gain valuable insights and drive strategic decision-making. With the growing complexity of data and the need for scalable infrastructure, many businesses are turning to multi-cloud strategies for handling their Big Data workloads. Understanding the nuances of multi-cloud deployment for Big Data is crucial for maximizing efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. In this article, we will explore the key considerations and benefits of adopting multi-cloud strategies in the context of Big Data analytics.
In today’s digital landscape, organizations are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies to harness the power of big data. With the rapid proliferation of information, businesses are faced with the challenge of managing, storing, and analyzing vast volumes of data across various cloud platforms. This article delves deep into the intricacies of multi-cloud strategies in relation to big data, exploring benefits, challenges, and best practices.
What is a Multi-Cloud Strategy?
A multi-cloud strategy involves leveraging multiple cloud service providers (CSPs) to meet an organization’s computing needs. This could mean using a combination of public clouds, private clouds, and even hybrid cloud solutions. By employing a multi-cloud approach, companies can avoid vendor lock-in, enhance system redundancy, and select the best services tailored to their specific requirements.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud Strategies for Big Data
1. Enhanced Flexibility
One of the primary advantages of a multi-cloud strategy is the flexibility it provides. Organizations can choose the best cloud services for their big data projects based on various factors like performance, pricing, and specific features. This adaptability enables businesses to switch providers seamlessly, ensuring they utilize the most effective tools available.
2. Improved Disaster Recovery
Utilizing multiple cloud providers enhances disaster recovery capabilities. If one cloud service fails, data can be accessed from another CSP, minimizing downtime and potential data loss. This redundancy is crucial for businesses that rely heavily on big data analytics and real-time data processing.
3. Cost Optimization
By strategically utilizing multiple cloud providers, organizations can optimize costs. Different providers offer varied pricing models, and businesses can select those that offer the best value for their specific workloads. This cost-effectiveness is a significant factor for businesses looking to maximize their return on investment in big data technologies.
4. Best-in-Class Services
Each cloud provider has its own specialized services tailored to specific big data needs. By adopting a multi-cloud strategy, companies can choose the best-in-class services for their analytics, storage, and processing needs, whether it’s using Google Cloud’s BigQuery, Amazon’s Redshift, or Microsoft Azure’s HDInsight.
Challenges of Implementing Multi-Cloud Strategies
1. Complexity in Management
While a multi-cloud approach offers numerous benefits, it also introduces complexity in managing multiple environments. Organizations need to establish robust governance policies, monitoring tools, and operational practices to handle their big data workloads effectively across different platforms.
2. Data Security and Compliance
Data security is paramount, especially in the realm of big data. With multiple cloud providers, organizations face challenges related to data governance, compliance with regulations (like GDPR or HIPAA), and ensuring data security measures are consistently applied across all platforms. Establishing a strong security framework is critical when managing sensitive information.
3. Integration Issues
Integrating services and datasets across different cloud platforms can pose significant challenges. Organizations need to ensure compatibility between various tools and technologies, which may require additional resources for data integration processes. Proper APIs and data connectors must be leveraged to create seamless workflows.
4. Increased Latency
Data transfer between multiple cloud platforms can introduce latency, affecting the speed and effectiveness of data processing and analytics workflows. It’s essential to consider geographic locations and the network capabilities of the chosen cloud providers to minimize latency issues.
Key Considerations for Multi-Cloud Big Data Strategies
1. Data Location and Sovereignty
Understanding where data is stored is critical for compliance and performance. Organizations must evaluate the locations of various cloud providers to ensure that they meet data sovereignty regulations. This consideration is vital to avoid legal complications and ensure that big data initiatives remain aligned with local laws.
2. Interoperability and Portability
When selecting cloud platforms, it’s essential to prioritize solutions that allow for interoperability and portability. This capability ensures that applications and data can move freely across different cloud environments without excessive modifications. Emphasizing open standards can facilitate this journey.
3. Vendor Lock-In Avoidance
A significant drawback of single-cloud strategies is the risk of vendor lock-in. Adopting a multi-cloud approach helps mitigate this risk by diversifying dependencies across multiple providers. Organizations can more easily negotiate terms and prices, which directly impacts their bottom line, particularly in big data services.
4. Scalability
Scalability is nothing short of essential for big data environments. Multi-cloud strategies allow businesses to scale their resources up or down based on changing needs. By using the strengths of different providers, organizations can efficiently manage their data workloads while minimizing costs.
Best Practices for Implementing Multi-Cloud Big Data Strategies
1. Develop a Clear Strategy
Organizations should begin by developing a clear multi-cloud strategy that outlines their objectives, policies, and guidelines for implementing big data initiatives across multiple providers. This strategy should involve key stakeholders, including IT, security, and compliance teams, to ensure comprehensive coverage.
2. Leverage Cloud Management Platforms
Utilize cloud management platforms (CMPs) to simplify monitoring, management, and governance of resources across various cloud environments. These tools enable organizations to streamline operations, reduce complexity, and maintain visibility over their big data assets.
3. Implement a Strong Security Framework
Implement robust security protocols that encompass all cloud environments. This includes performing regular audits, utilizing encryption, and applying identity and access management (IAM) practices to ensure data security throughout the multi-cloud ecosystem.
4. Monitor Performance and Cost
Constantly monitor the performance and costs associated with each cloud provider. Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) and utilizing analytics tools will help maintain an efficient multi-cloud strategy while ensuring that big data initiatives deliver expected results without overspending.
5. Foster a Culture of Collaboration
Encourage collaboration between teams involved in big data initiatives. Facilitating cross-departmental communication ensures that insights and methodologies are shared, which fosters innovation and improves overall strategy execution across different cloud platforms.
Conclusion
The increasing adoption of multi-cloud strategies for big data is reshaping how organizations manage and analyze their data. By understanding the benefits and challenges associated with this approach, organizations can strategically leverage multiple cloud environments to optimize their big data endeavors and position themselves for future growth in an increasingly data-driven world.
Embracing multi-cloud strategies for big data offers organizations the flexibility, scalability, and resilience needed to effectively manage and analyze large datasets. By leveraging multiple cloud providers, businesses can optimize performance, reduce costs, and enhance their data processing capabilities, ultimately gaining a competitive edge in the ever-evolving landscape of big data analytics.