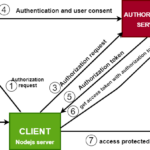
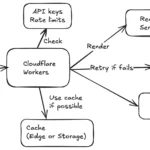
An API rate spike occurs when an application receives a sudden and significant increase in the volume of API requests. This can put a strain on the server, leading to latency issues, downtime, and potential service disruptions. To handle an API rate spike effectively, it is important to implement strategies such as rate limiting, caching, load balancing, and scaling resources dynamically. Monitoring and analyzing API usage patterns can also help in identifying potential spikes early on and taking proactive measures to mitigate their impact. By implementing these techniques, organizations can ensure the resilience and reliability of their APIs and web services during periods of high demand.
Understanding API usage is crucial for developers and organizations that rely on APIs for their services. An API rate spike refers to a sudden surge in the number of requests made to an API within a specific timeframe. This phenomenon can significantly affect the performance and availability of an API, leading to potential disruptions in service and negative user experiences. In this article, we will explore the causes of API rate spikes, their implications, and effective strategies to handle and mitigate their impact.
What Causes an API Rate Spike?
There are several factors that can result in an API rate spike. Understanding these factors can help developers anticipate and respond to such occurrences effectively.
1. Seasonal Traffic Changes
Many businesses experience unpredictable surges in traffic during specific periods, such as holidays, sales events, or product launches. These seasonal traffic changes can lead to a sudden increase in API requests.
2. Bot Crawling and Scraping
Automated scripts or bots may crawl your API for data or content. If not properly managed, these bots can generate a large number of requests in a short period, leading to a rate spike.
3. Mobile App Updates
A new version of a mobile app may inadvertently increase API usage due to updated features or functionalities. If many users simultaneously update their apps, it may result in a spike in demand on the API end.
4. Marketing Campaigns
Launching targeted marketing campaigns that drive traffic to specific services can also cause a temporary surge in API traffic when many users interact with the service simultaneously.
5. System Issues and Bugs
A bug in the application code can lead to repeated, unintended API calls, effectively creating a rate spike. Developers must ensure thorough testing to mitigate this risk.
Implications of API Rate Spikes
When an API experiences a rate spike, various issues can arise, including:
1. Throttling and Rate Limiting
Many APIs implement throttling or rate limiting strategies to control the number of requests. When a rate spike occurs, legitimate users may find themselves temporarily blocked from access, affecting their experience.
2. Service Degradation
A sudden influx of requests can lead to service degradation, where response times increase, or services become temporarily unavailable. This situation can impact business operations and user satisfaction.
3. Increased Operational Costs
Handling a sudden surge in API requests can lead to elevated operational costs, particularly in terms of server resources, bandwidth, and necessary scaling measures.
4. Impact on Overall API Reliability
If an API cannot handle the load, it risks being perceived as unreliable, which can damage its reputation and result in lost users or customers.
How to Handle API Rate Spikes Effectively
While unexpected rate spikes can destabilize API performance, there are effective strategies that organizations can implement to manage such situations.
1. Implement Rate Limiting
Establish clear rate limiting policies to control the number of requests a user or application can make in a specified time period. By defining these limits, you can ensure fair use and protect your API from overload.
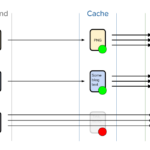
2. Utilize Caching Strategies
Implementing caching mechanisms can greatly reduce the load on your API during traffic spikes. By storing frequently requested data for a short period, you can minimize the number of times your API needs to retrieve information from the backend, improving response times and reducing server load.
3. Analyze Usage Patterns
Regularly analyze API usage data to identify patterns that may indicate potential spikes. By understanding user behavior, you can forecast and prepare for future surges. Employing tools for API monitoring can provide invaluable insights into real-time usage and performance metrics.
4. Scale Infrastructure
Investing in scalable architecture is crucial for handling increased traffic. Utilizing cloud-based services allows for elastic scaling, enabling your infrastructure to automatically adjust to handle varying loads. This means you can allocate more resources in times of high demand without affecting performance.
5. Optimize API Performance
Regularly optimize your API performance by reviewing your endpoints, response sizes, and data structures. Improving efficiency can help your API handle larger volumes of requests with minimal latency.
6. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Employing a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can enhance the distribution of API content globally, reducing latency and server load by serving content from the nearest location to the user. This can be particularly beneficial during traffic spikes.
7. Establish a Communication Plan
It’s essential to establish a proactive communication plan to inform users about potential rate limits or service interruptions during high-traffic events. Keeping users informed can mitigate frustration and improve user experience.
8. Throttle Non-Critical Requests
Identify and separate critical and non-critical requests so that you can prioritize important functionalities during a rate spike. This step ensures that crucial services remain operational even under high demand.
9. Develop an Incident Response Plan
Finally, it’s essential to have an incident response plan in place. This plan should outline steps to take when a rate spike occurs, including measures for scaling infrastructure, updating user communications, and conducting post-mortem analyses to avoid similar issues in the future.
Conclusion
While managing an API rate spike can be challenging, it is important for organizations that rely on APIs and web services. By implementing proper strategies—such as rate limiting, caching, and infrastructure scaling—developers can effectively minimize the impact of these spikes, ensuring a persistent, reliable service for all users. Understanding API usage and preparing for unexpected demands can lead to a smoother, more efficient management of web services and a better experience for users.
An API rate spike refers to a sudden increase in the number of requests made to an API, potentially causing performance issues or downtime. To handle it effectively, API providers can implement rate limiting, caching mechanisms, and scaling resources to accommodate the increased demand while maintaining service reliability and performance. Monitoring and analyzing API usage trends can also help identify and address potential rate spikes proactively. By employing these strategies, API providers can ensure a seamless and uninterrupted user experience during periods of high demand.